- The paper evaluates reproducibility issues in four BERT-based metrics, highlighting how subtle preprocessing changes affect results.
- Methodology involved empirical sensitivity analyses of tokenization, punctuation removal, and dataset-specific IDF-weighting across language pairs.
- Findings emphasize the need for transparent documentation and standardized practices to improve reliability in natural language generation evaluations.
Analyzing "Reproducibility Issues for BERT-based Evaluation Metrics"
The paper "Reproducibility Issues for BERT-based Evaluation Metrics" seeks to explore the reproducibility challenges inherent in BERT-based evaluation metrics particularly used in natural language generation (NLG) tasks, including machine translation (MT). It investigates the reproducibility of four well-regarded BERT-based metrics, identifies preprocessing and infrastructural issues affecting reproducibility, and conducts sensitivity analyses of preprocessing effects.
Introduction to Reproducibility in BERT-based Metrics
Reproducibility is a critical issue in ML and NLP, impacting experimental trust and reliability. This paper acknowledges the reproducibility crisis identified by several sources, emphasizing the need for reproducible results in NLG metrics. While BLEU, a traditional metric, is noted for its reproducibility issues, newer BERT-based metrics are believed to have improved. However, this paper identifies several obstacles in reproducing results and verifies these challenges through empirical examination.
Reproduction of BERT-based Metrics
Metrics Under Review
The paper evaluates four BERT-based metrics: BERTScore, MoverScore, BaryScore, and SentSim, which are used across various NLG tasks such as MT, summarization, and image captioning. These metrics reportedly outperform lexical-based metrics like BLEU. The focus is placed on their reproducibility across different tasks:
- BERTScore: Calculates token-level similarities using BERT embeddings.
- MoverScore: Employs Word Mover Distance to gauge semantic similarities.
- BaryScore: Utilizes Wasserstein Barycenter for embeddings.
- SentSim: Evaluates cross-lingual semantic alignment.
Experimental Results and Observations
The paper rigorously tests these metrics, revealing several reproducibility issues often influenced by:
- Undocumented preprocessing
- Variability in reported competitor scores
- Missing code/documentation
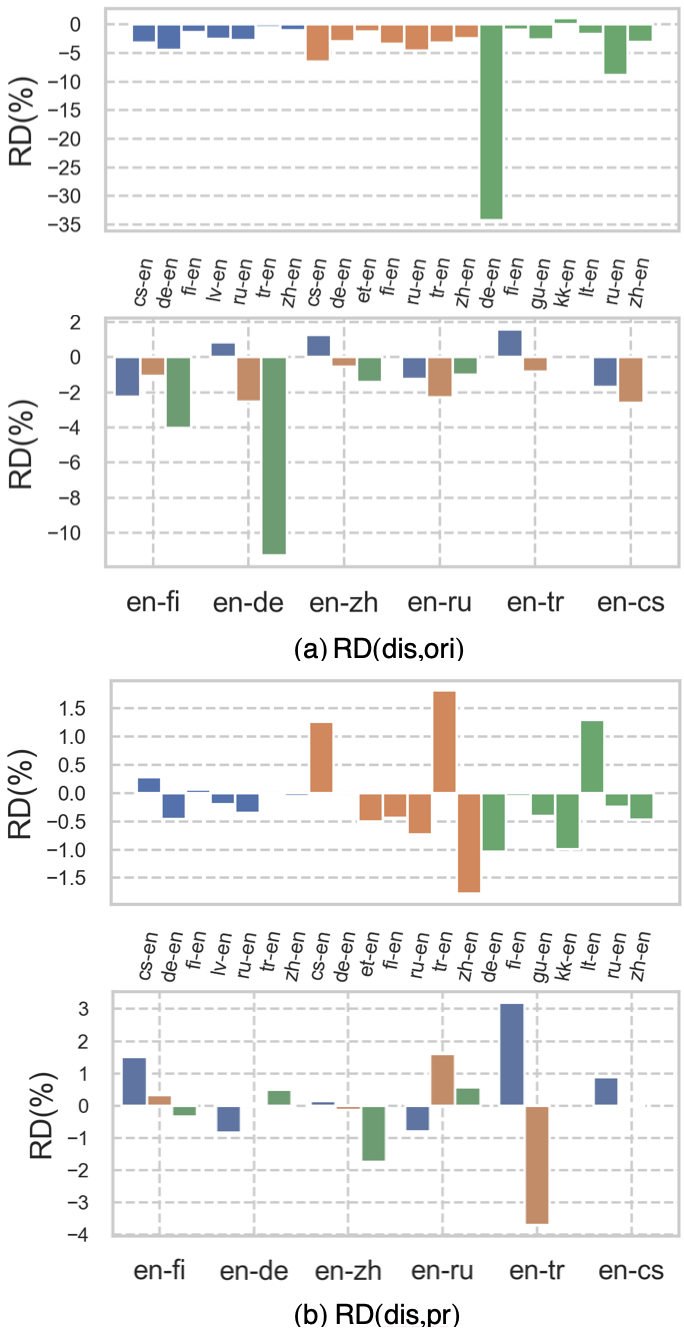
The experiments demonstrate that even minor undocumented preprocessing changes can substantially affect evaluation outcomes, complicating reproducibility in MT datasets, as exemplified below.
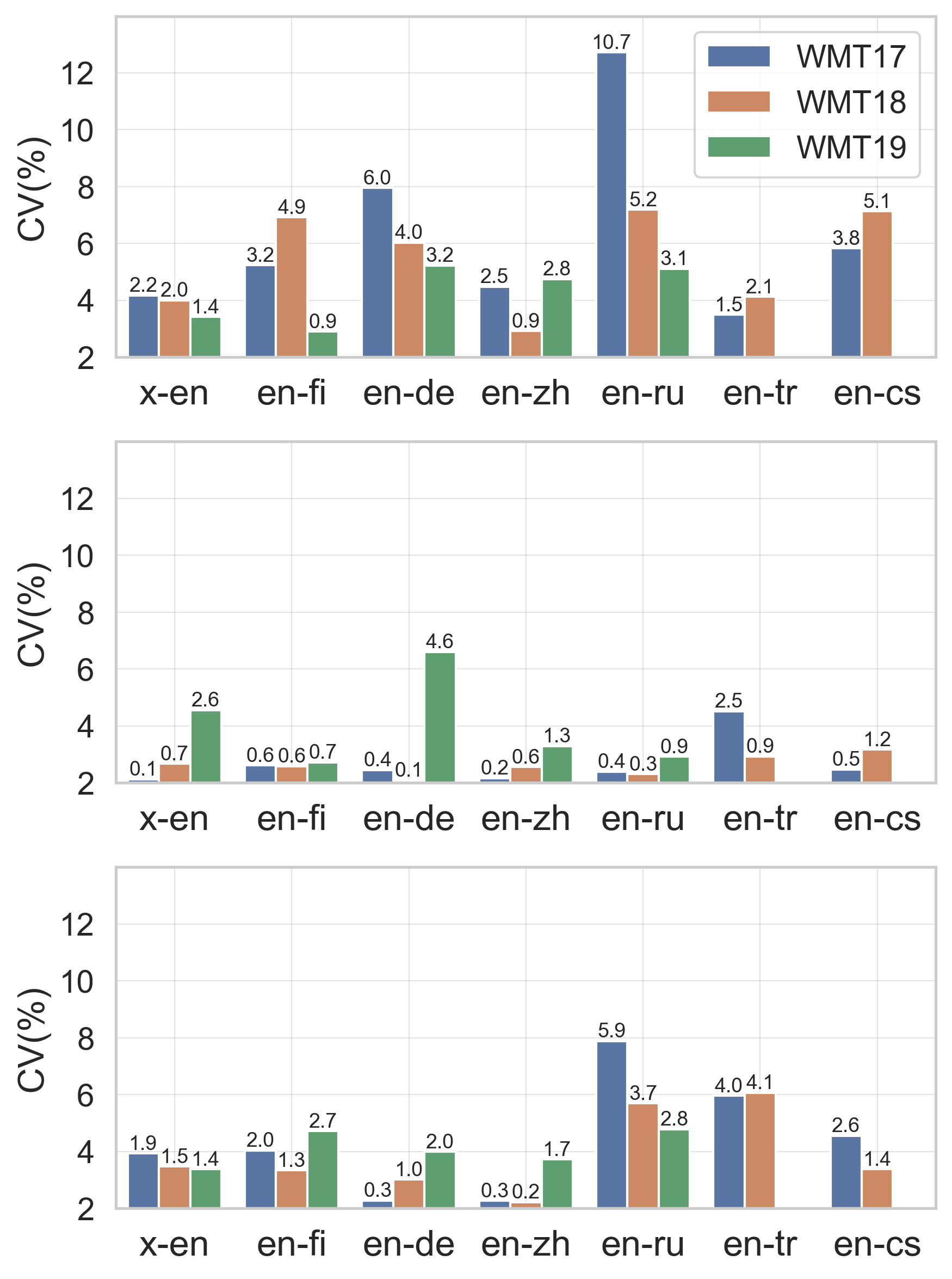
Figure 1: CVSTOP for different BERT-based metrics across various language pairs.
Sensitivity Analysis
Preprocessing Impact
The paper provides an extensive analysis of various preprocessing techniques such as tokenization, punctuation removal, stopwords filtering, and IDF-weighting. It highlights that:
Variability Across Languages
Diversified experiments over multiple language pairs suggest that reproducibility issues are exacerbated in morphologically rich languages like Finnish and Turkish.
Discussion
The study critiques the current inability of reproducibility in BERT-based metrics compared to their reported performance when established methodologies and configurations are not clearly accessible or consistently applied. Practical recommendations are provided for improving reproducibility standards, which include:
- Emphasizing transparency in preprocessing documentation.
- Encouraging authors to release complete implementations, including scripts and configurations.
- Recommending uniform preprocessing practices across different metric evaluations.
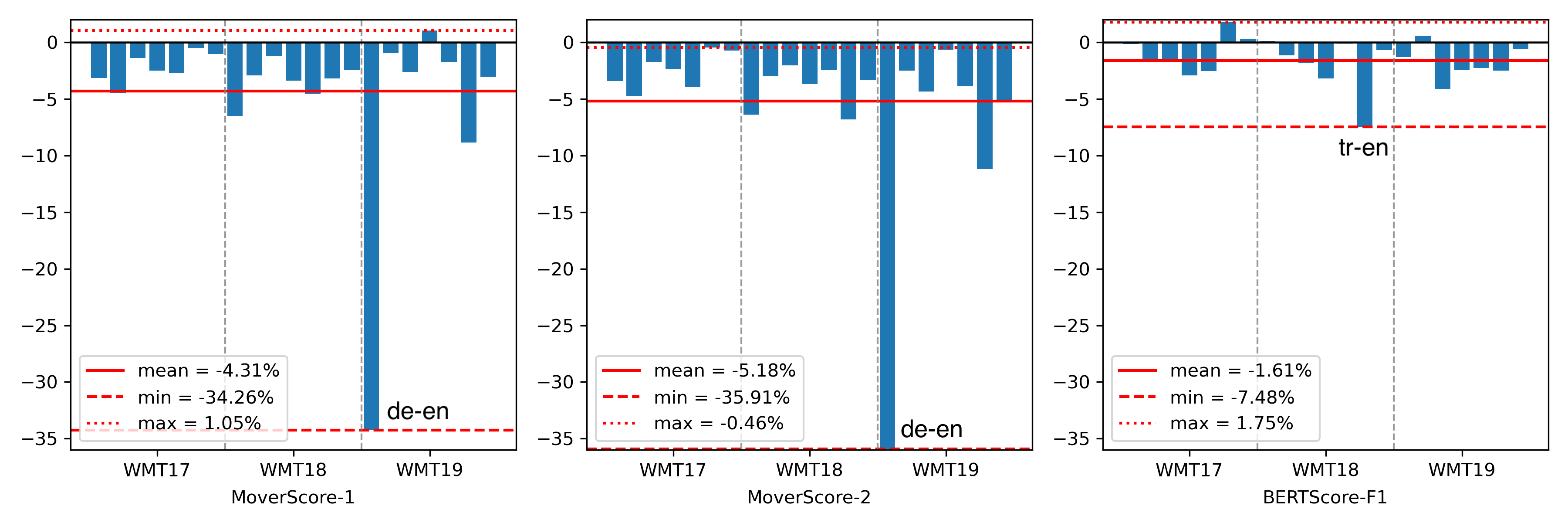
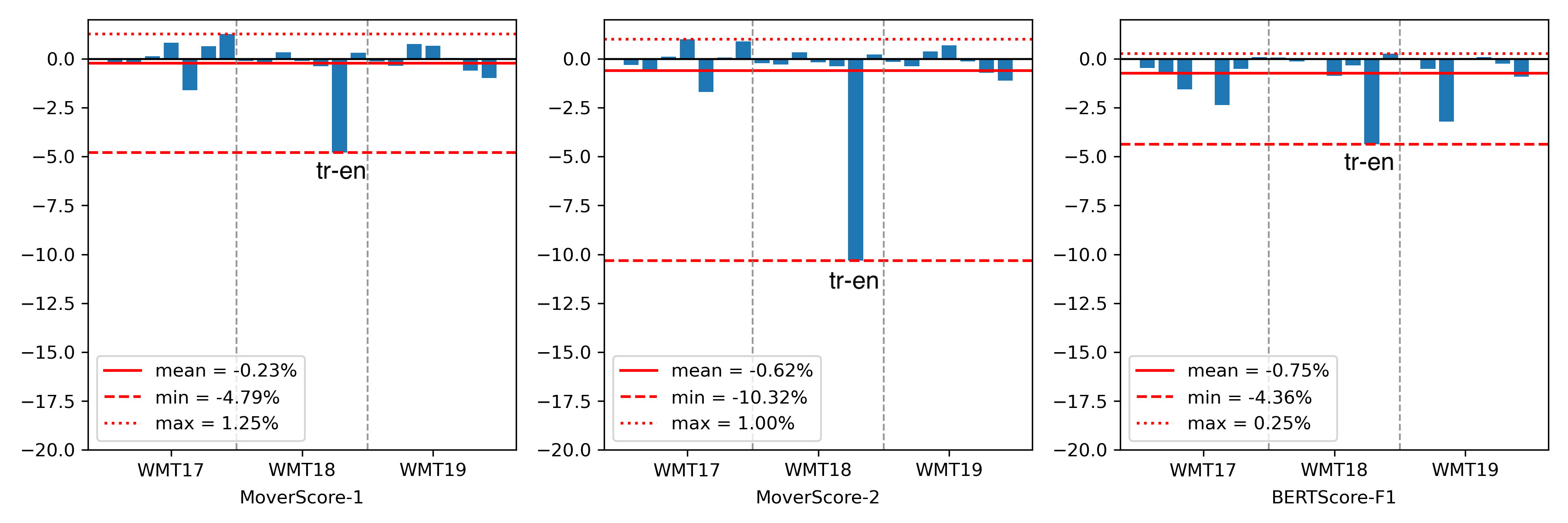
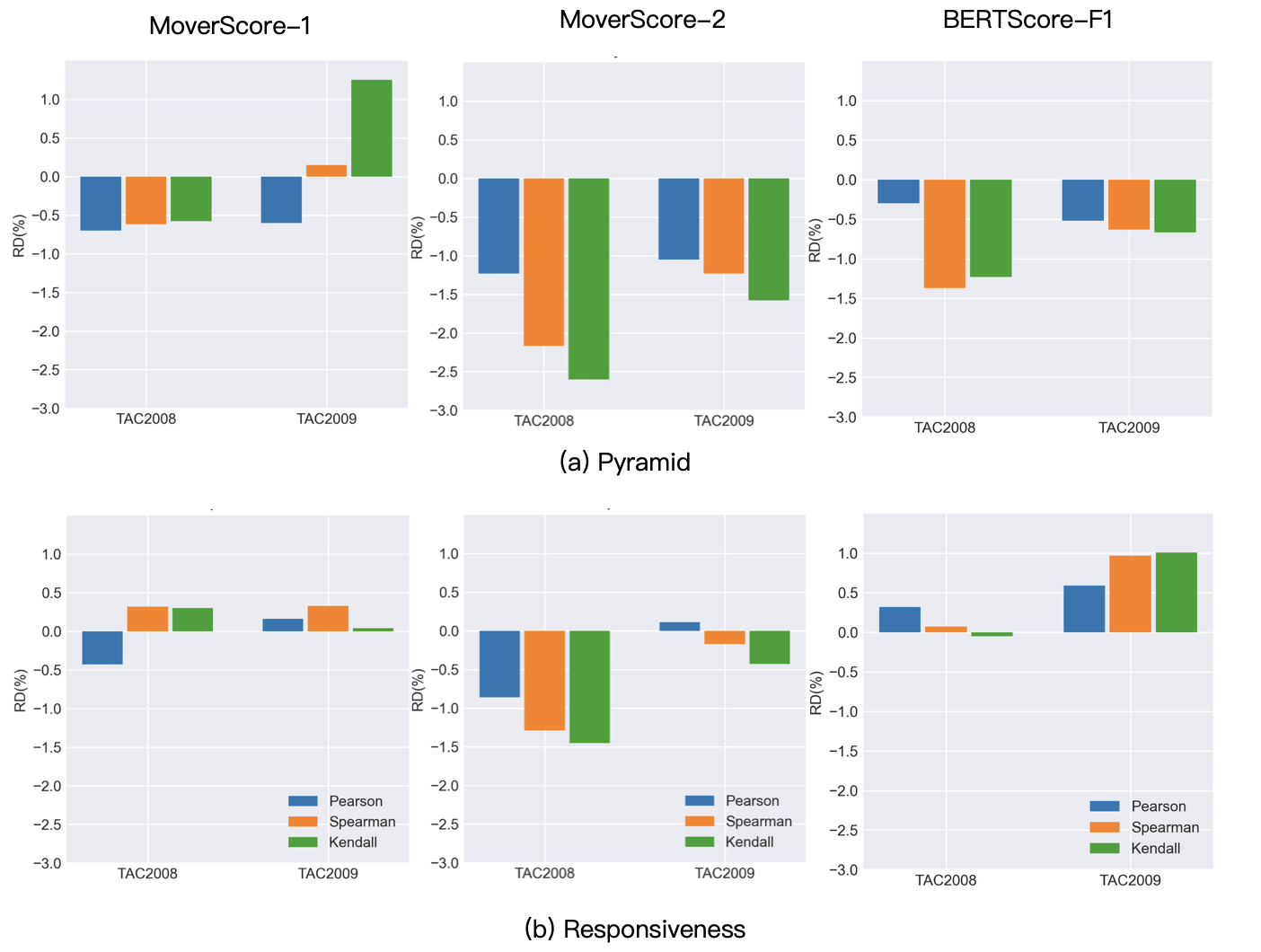
Figure 3: Variations in performance metrics (WMT17-19) with and without proper IDF-weighting.
Conclusion
The paper concludes that although some progress has been made towards reproducibility in NLP metrics, considerable work is still necessary. The over-reliance on certain preprocessing methods points to deeper systemic issues in reproducibility. Moving forward, a consolidated approach involving detailed documentation, standard practices, and open access to resources is essential for reliable evaluation metrics in AI research, ensuring consistency across different experiments and studies.