Dataset Distillation by Matching Training Trajectories
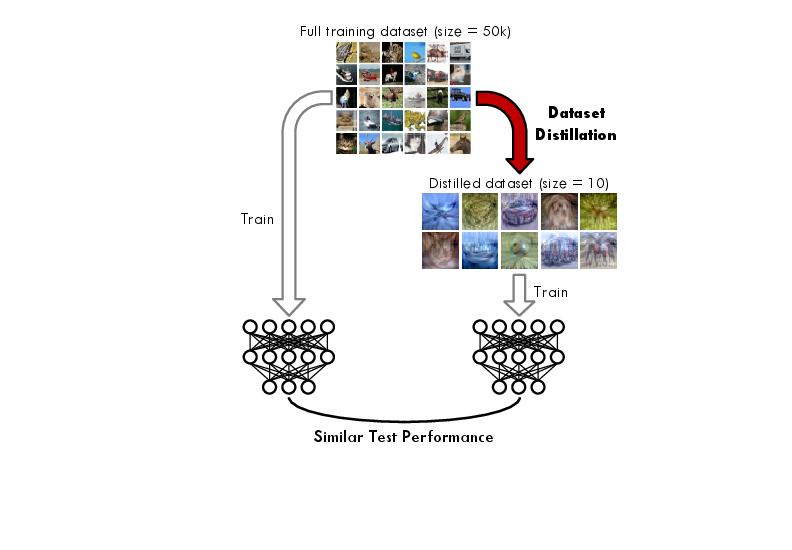
Abstract: Dataset distillation is the task of synthesizing a small dataset such that a model trained on the synthetic set will match the test accuracy of the model trained on the full dataset. In this paper, we propose a new formulation that optimizes our distilled data to guide networks to a similar state as those trained on real data across many training steps. Given a network, we train it for several iterations on our distilled data and optimize the distilled data with respect to the distance between the synthetically trained parameters and the parameters trained on real data. To efficiently obtain the initial and target network parameters for large-scale datasets, we pre-compute and store training trajectories of expert networks trained on the real dataset. Our method handily outperforms existing methods and also allows us to distill higher-resolution visual data.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Glossary
- Back-propagation: A method for computing gradients through a sequence of operations to update parameters during training. "and back-propagate through the training iterations."
- Behavior cloning: An imitation learning approach that trains a policy to mimic expert actions directly. "Behavior cloning trains the learning policy to act the same as expert demonstrations."
- Bi-level optimization: An optimization framework with nested objectives (an inner and outer problem), often used to select or tune model components. "new formulations based on bi-level optimization have shown promising results on applications like continual learning"
- Catastrophic mode collapse: A failure mode in generative or synthesis processes where outputs lose diversity and collapse into a few modes. "degrading to catastrophic mode collapse in the worst case."
- Continual learning: Training that aims to learn a sequence of tasks without forgetting earlier ones. "including continual learning"
- Coreset: A small, representative subset of data designed to preserve performance when training on it instead of the full set. "coreset and instance selection aim to select a subset of the entire training dataset"
- Coreset selection: The process of choosing a coreset from the full dataset to enable efficient training. "Comparing distillation and coreset selection methods."
- Cosine distance: A similarity measure based on the cosine of the angle between two vectors, used as a loss or metric. "such as a cosine distance"
- Dataset distillation: Synthesizing a small dataset so that models trained on it match the performance of training on the full dataset. "Dataset distillation is the task of synthesizing a small dataset such that a model trained on the synthetic set will match the test accuracy of the model trained on the full dataset."
- Differentiable augmentation: Data augmentation operations that are differentiable, allowing gradients to pass through them to optimize inputs. "where is the differentiable augmentation technique"
- Differentiable Siamese Augmentation: A differentiable augmentation scheme that applies matched transformations to pairs of inputs; here not used during distillation. "Our method does not use differentiable Siamese augmentation since there is no real data used during the distillation process;"
- Distribution matching: Aligning the synthetic data distribution to the real data distribution without modeling optimization steps. "instead focusing on distribution matching between synthetic and real data."
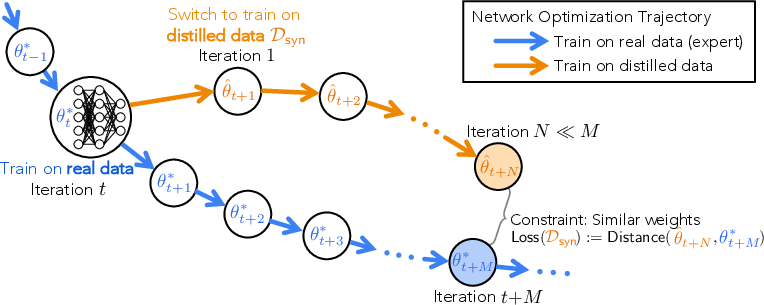
- Expert trajectories: Recorded sequences of model parameters from training on real data, used as targets for imitation. "using expert trajectories to guide the distillation of our synthetic dataset."
- Federated learning: Training models across decentralized data sources without centralizing raw data. "federated learning"
- Generative model: A model that learns to produce realistic data samples from a learned distribution. "A related line of research learns a generative model to synthesize training data"
- Gradient matching: A technique that aligns gradients from synthetic data with those from real data to amplify learning signals. "amplifying learning signal via gradient matching"
- Hyperparameter optimization: Gradient-based or search-based tuning of training hyperparameters to improve performance. "optimized them using gradient-based hyperparameter optimization"
- Imitation learning: Learning a policy by mimicking expert demonstrations or behaviors. "Imitation learning attempts to learn a good policy by observing a collection of expert demonstrations"
- Infinite-width kernel limit: The regime where neural networks behave like kernel machines as width goes to infinity, enabling analytical training via kernels. "optimizing with respect to the infinite-width kernel limit"
- Instance normalization: A normalization technique that normalizes feature maps per-instance, often used in vision models. "Instance normalization"
- Instance selection: Choosing specific training examples to form a smaller, effective training set. "coreset and instance selection aim to select a subset of the entire training dataset"
- Kernel Inducing Point (KIP): A method that distills data using kernel techniques derived from the infinite-width limit. "Kernel Inducing Point (KIP) performs distillation using the infinite-width network limit."
- Logits: The raw, pre-softmax outputs of a classifier used to compute probabilities. "a single linear layer produces the logits."
- Meta-learning: Learning to learn; frameworks that optimize across tasks to improve learning efficiency. "meta-learning research"
- Model distillation: Transferring knowledge from a large or complex model to a smaller one. "Hinton et al.~\cite{hinton2015distilling} proposed model distillation"
- Neural architecture search: Automatically discovering model architectures that perform well for a given task. "neural architecture search"
- Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK): A kernel that characterizes infinite-width neural networks, enabling kernel-based training approximations. "where the distilled data is learned with respect to the Neural Tangent Kernel"
- Parameter space: The high-dimensional space comprising all trainable parameters of a model. "in the parameter space"
- Parameter trajectory: The sequence of parameter states a model follows during training. "matching segments of parameter trajectories trained on synthetic data"
- Privacy-preserving ML: Methods that protect sensitive information while training machine learning models. "privacy-preserving ML"
- SGD with momentum: An optimizer that accelerates SGD by accumulating a velocity vector to damp oscillations and speed convergence. "We use SGD with momentum to optimize and "
- Training dynamics: The behavior and evolution of model parameters during optimization. "directly imitate the long-range training dynamics of networks trained on real datasets."
- Trajectory matching: Aligning the learned parameter trajectory on synthetic data with an expert trajectory from real data. "Dataset Distillation via Trajectory Matching"
- Weight matching loss: An objective that penalizes differences between student and expert parameters to guide synthetic data optimization. "update our distilled images according to the weight matching loss:"
- ZCA whitening: A decorrelation and whitening transform that removes linear correlations in data while preserving variance. "we employ ZCA whitening as done in previous work"
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.