- The paper introduces self-consistency, a method that samples multiple reasoning paths to aggregate the most frequent answer from chain-of-thought prompts.
- It employs an unsupervised sample-and-marginalize approach, significantly improving accuracy on benchmarks like GSM8K and commonsense reasoning tasks.
- The method outperforms traditional greedy decoding, sample-and-rank, and beam search by effectively exploring reasoning diversity for robust outcomes.
Overview of Self-Consistency in Chain of Thought Reasoning
Self-consistency is a novel decoding strategy designed to enhance the reasoning capabilities of LLMs within the framework of chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting. Traditional CoT prompting involves issuing sequential thought processes to arrive at an answer, typically relying on greedy decoding methods. However, greedy decoding often limits the exploration of alternative reasoning pathways, thereby restricting the model's effectiveness in complex reasoning tasks. Self-consistency addresses this limitation by introducing a "sample-and-marginalize" approach, where multiple reasoning paths are sampled, and the final decision is made based on consistency among these alternatives.
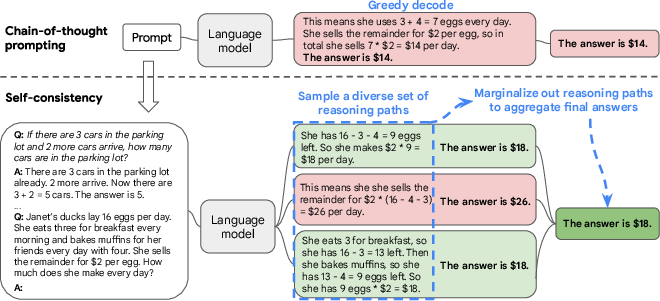
Figure 1: The self-consistency method contains three steps: (1) prompt a LLM using chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting; (2) replace the ``greedy decode'' in CoT prompting by sampling from the LLM's decoder to generate a diverse set of reasoning paths; and (3) marginalize out the reasoning paths and aggregate by choosing the most consistent answer in the final answer set.
Methodology
The self-consistency method comprises several steps, beginning with chain-of-thought prompting. Unlike traditional methods where the optimal reasoning path is greedily decoded, self-consistency employs sampling from the LLM’s decoder to generate diverse reasoning paths. Each of these paths may lead to different answers. To arrive at the most reliable and consistent outcome, self-consistency marginalizes over these paths and selects the answer that appears most consistently across the samples. A key advantage of this method is its unsupervised nature, allowing it to function directly with pre-trained models without additional annotation or fine-tuning.


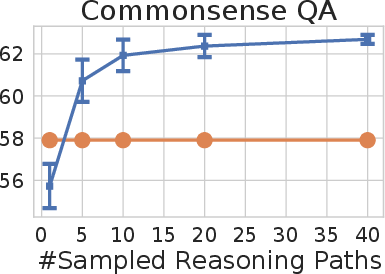

Figure 2: Self-consistency (blue) significantly improves accuracy over CoT-prompting with greedy decoding (orange) across arithmetic and commonsense reasoning tasks, over LaMDA-137B. Sampling a higher number of diverse reasoning paths consistently improves reasoning accuracy.
Empirical Evaluation
Extensive empirical evaluations demonstrate that self-consistency yields substantial improvements over traditional CoT prompting across various benchmarks, including arithmetic reasoning (GSM8K, SVAMP, AQuA) and commonsense reasoning (StrategyQA, ARC-challenge). Notably, the method achieved an impressive 17.9% absolute accuracy increase on GSM8K, underscoring its effectiveness in complex reasoning tasks.
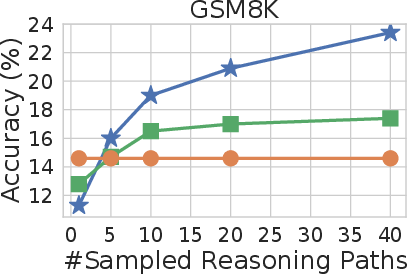
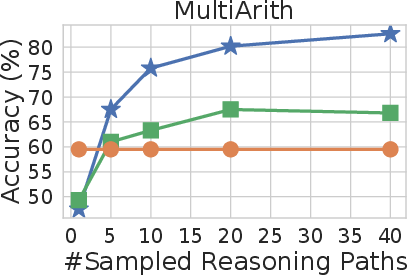
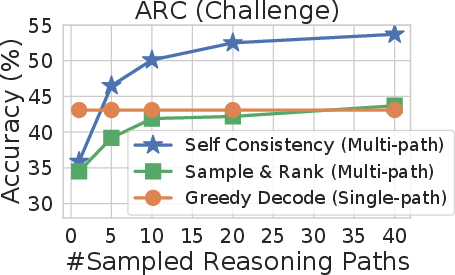
Figure 3: Self-consistency significantly outperforms sample-and-rank with the same # of samples.
Comparison with Existing Methods
Self-consistency offers significant advantages over existing methods such as sample-and-rank and beam search. Unlike sample-and-rank, which merely selects the highest-ranked sample, self-consistency aggregates over multiple samples to ensure reliability and consistency in the final answer. Beam search, while promoting diversity to some extent, often falls short in comparison to self-consistency due to less effective exploration of reasoning diversity.
Implications and Future Developments
The implications of self-consistency in AI are profound, offering a promising avenue for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Its unsupervised nature and compatibility with existing models without requiring additional training make it a versatile tool. Future research could explore the amalgamation of self-consistency with other model architectures and the expansion of its applications across diverse NLP tasks.


Figure 4: GSM8K accuracy over LaMDA-137B. Self-consistency works under various sampling strategies and sampling parameters.
Conclusion
Self-consistency represents a significant advancement in the decoding strategies for reasoning tasks. By leveraging diverse reasoning paths and focusing on answer consistency, it effectively mitigates the limitations of greedy decoding, offering robust improvements across various reasoning benchmarks. The method stands out for its simplicity, efficacy, and unsupervised approach, setting a new direction for future research in enhancing the capabilities of pre-trained LLMs.











