- The paper introduces a crafted noise-based training method that significantly enhances the adversarial robustness of deep spiking neural networks.
- It achieves up to 13.7% improvement under FGSM and 10.1% under PGD attacks on CIFAR datasets while maintaining high accuracy on clean images.
- Energy analyses confirm that HIRE-SNN offers substantial computational savings, making SNNs viable for low-power, safety-critical AI applications.
Harnessing Robust SNNs via Crafted Noise Training
Introduction
"HIRE-SNN: Harnessing the Inherent Robustness of Energy-Efficient Deep Spiking Neural Networks by Training with Crafted Input Noise" explores the potential of deep spiking neural networks (SNNs) for energy-efficient computation while addressing adversarial robustness. Spiking neural networks promise computational efficiency on neuromorphic hardware, but their resilience against adversarial attacks has been under-analyzed due to training cost constraints. This research outlines a method to enhance SNN robustness without additional computational overhead by leveraging crafted input noise.
Analysis of Inherent SNN Robustness
Despite claims of inherent robustness in SNNs against adversarial attacks, comprehensive evaluations had been restricted to small datasets and shallow networks. Previous studies suggested that rate-coded SNNs possess robustness due to sparse activation maps, but our analysis extends to deeper networks trained on direct inputs. The findings reveal that deep, low-latency SNNs generally show lower spike activity yet higher time-averaged spiking activity (TASA), a crucial extension to previous robustness observations. This is visualized through the layer-wise average spikes and TASA in SNNs compared to ANNs.
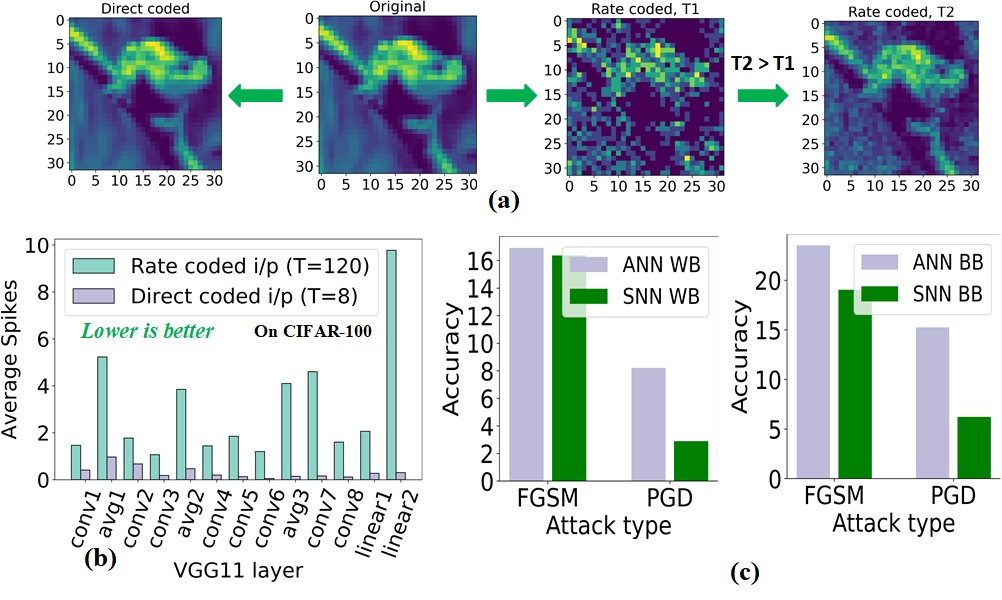
Figure 1: (a) Direct and rate-coded input variants of the original image. (b) Layer-wise average spikes for VGG11. (c) Performance of direct-input VGG11 SNN and its equivalent ANN under various white-box (WB) and black-box (BB) attacks on CIFAR-100.
The presented method ("HIRE-SNN") employs a spike-timing-dependent backpropagation (STDB) approach that introduces noise into input data across defined time steps, enhancing robustness without additional training iterations. Noise crafting uses linear surrogate gradients for backpropagation and input perturbations, optimizing weight, threshold, and leak parameters over dynamic periods. This method exploits the temporal dynamics of SNNs while maintaining clean image accuracy, demonstrated through empirical analysis.
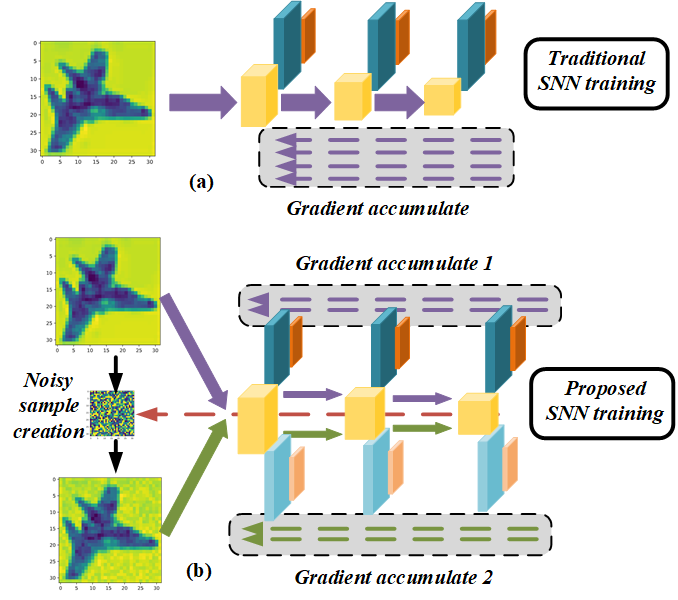
Figure 2: (a) Traditional training scheme vs (b) proposed training scheme, highlighting different activation maps and gradient calculations using direct inputs with introduced noise.
Robustness and Training Validation
Empirical evaluations on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 using VGG and ResNet architectures demonstrate significant robustness improvements. HIRE-SNN-trained SNNs showed up to 13.7% and 10.1% improvements in classification accuracy on FGSM and PGD attacks, respectively, while exhibiting minimal loss on clean images. The models outperform rate-coded SNNs, achieving lower latency and computation energy bounds, affirming computational efficiency motives.
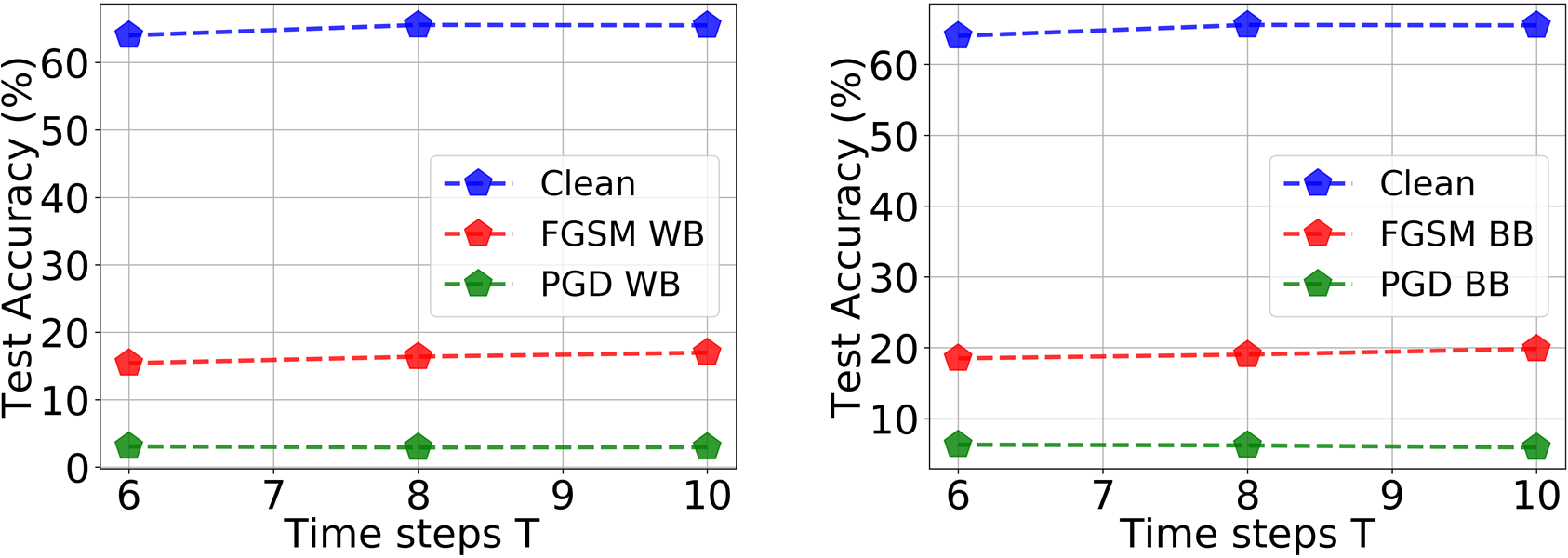
Figure 3: Classification performance of VGG11 on CIFAR-100 as number of time steps T varies.
Crucially, SNNs trained under this scheme do not exhibit gradients obfuscation artifacts, as confirmed through gradient augmentation tests. This further validates the authenticity of the robustness ascribed to the crafted noise training scheme, ruling out misleading gradient masking effects.
Energy Efficiency and Compute Cost Analysis
HIRE-SNN's computational energy analysis highlights substantial efficiency gains, with performance on-par with ANNs' accuracy. With assumptions of 32-bit floating-point and integer operations, the approach exhibited significant energy savings over traditional SNNs, consolidating the promise of SNNs for resource-constrained environments.
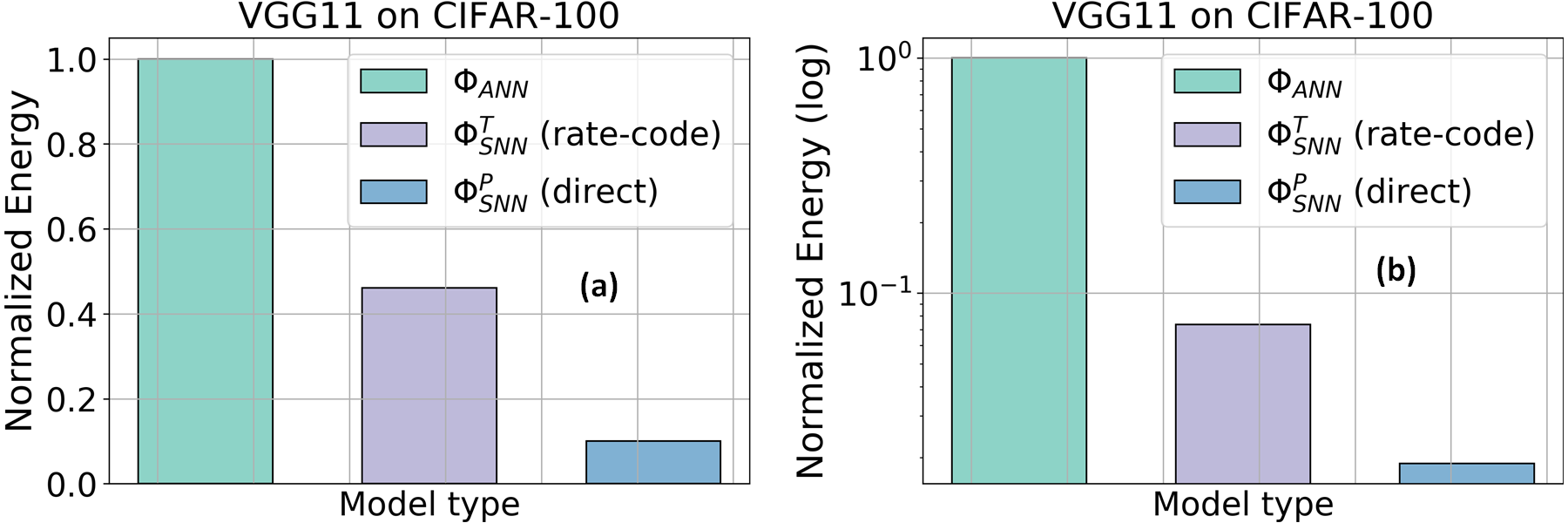
Figure 4: Comparison of normalized compute energy computed assuming (a) 32-bit FP and (b) 32-bit INT implementations.
Conclusion
The paper demonstrates that by careful design of training inputs and leveraging the temporal computation timeline of SNNs, one can amplify the natural robustness inherent to spiking architectures. HIRE-SNN points towards a viable route for constructing energy-efficient SNNs, tailored to withstand adversarial aggressions effectively, thus enhancing their appeal for reliable, low-power AI applications in safety-critical systems. Future exploration will focus on scaling these insights to more complex networks and additional adversarial scenarios to fortify SNN defenses against a broader range of threats.





