- The paper introduces the DSDI framework, integrating domain-specific and domain-invariant features to improve generalization on unseen domains.
- It employs adversarial training and meta-learning to disentangle and optimize feature representations, with experiments demonstrating superior performance on benchmarks like PACS and DomainNet.
- Ablation studies confirm the critical role of balancing these features, as removal of meta-learning or disentanglement components leads to significant performance drops.
Exploiting Domain-Specific Features to Enhance Domain Generalization
Introduction
The paper "Exploiting Domain-Specific Features to Enhance Domain Generalization" (2110.09410) presents a novel approach to domain generalization (DG), a critical task in machine learning where models trained on multiple source domains must effectively generalize to unseen target domains. Traditional DG methods emphasize domain-invariant features, often neglecting domain-specific information that can significantly enhance generalization performance. This paper introduces the Domain Specific-Domain Invariant (DSDI) framework, which leverages both domain-invariant and domain-specific features within a unified meta-learning paradigm.
Methodology
Theoretical Foundation
The paper's theoretical framework is rooted in the information bottleneck principle, which suggests capturing minimal sufficient statistics that retain essential information while discarding irrelevant details. The authors propose distinct definitions for domain-invariant and domain-specific mappings within this paradigm:
- Domain-Invariant Representation: Extracted features remain consistent across different domains, ensuring stability across domain shifts.
- Domain-Specific Representation: Features unique to each domain that potentially improve model adaptability to unseen domains.
Supported by a theoretical analysis and empirical demonstrations, the paper argues that incorporating domain-specific information can enhance predictive performance, particularly when the target's domain-specific features provide label-relevant context.
DSDI Framework
The DSDI framework achieves this dual feature extraction through disentangled learning:
- Adversarial Training for Domain-Invariance: Employs a domain discriminator that maximizes domain label prediction while the feature extractor minimizes it, ensuring domain-invariance.
- Meta-Learning for Domain-Specific Features: Utilizes a meta-learning procedure to enhance domain-specific features' capacity to adapt to target domains, isolating them from domain-invariant features by minimizing their covariance.
- Learning and Inference: The framework integrates both representations into a classifier optimized via cross-entropy, supporting robust generalization through meta-optimization.
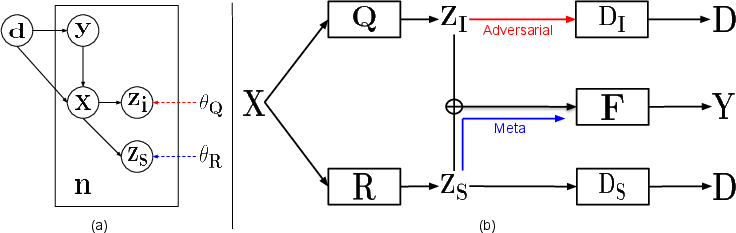
Figure 1: The graphical model (a) and overall architecture (b) for our proposed DSDI framework highlight its key components and interactions.
Experiments
Benchmark Evaluation
The paper evaluates the DSDI framework on several benchmark datasets, including PACS, VLCS, and DomainNet. The results demonstrate that DSDI consistently matches or surpasses state-of-the-art methods across various DG challenges, particularly excelling in tasks where domain-specific information enhances class distinction.
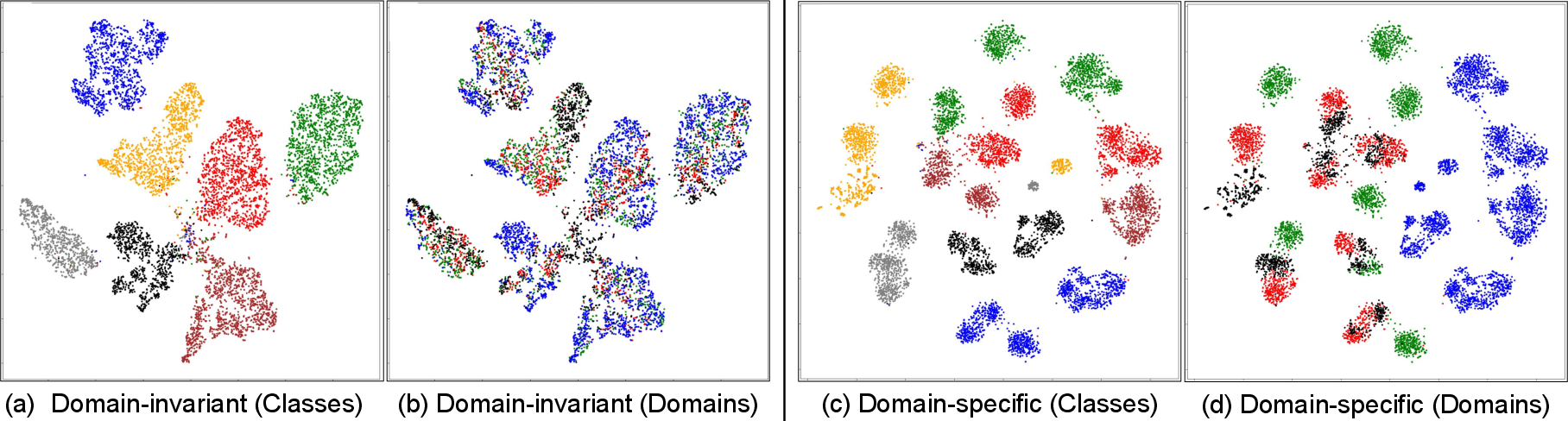
Figure 2: Feature visualization underscores domain-specific and domain-invariant disentanglement across domains and classes in the PACS dataset.
The performance advantages are most pronounced when domain-specific information is closely tied to class labels, as in the case of environments where background features can indicate particular class membership.
Ablation Study
To further validate the model, the authors conduct an ablation paper using their generated Background-Colored-MNIST dataset, where domain-specific features are color-coded backgrounds correlating with class labels. The paper confirms the importance of both disentangled learning and meta-training on domain-specific features, illustrating significant performance drops when these components are removed.
Discussion
The paper outlines several implications and future directions:
- Balancing Domain Representations: The success of DSDI highlights the need for a nuanced balance between domain-invariant and domain-specific features.
- Meta-Learning Optimization: Meta-learning is essential for adapting domain-specific features, especially when transferring knowledge to new, unseen domains.
- Potential Limitations: While the approach demonstrates considerable promise, the efficacy of domain-specific features might decrease if these features correlate with different class labels in target domains compared to sources.
Conclusion
The paper succeeds in challenging the traditional focus on domain-invariant features by demonstrating that domain-specific information, when properly applied and balanced, can significantly enhance the robustness and adaptability of models in domain generalization tasks. The DSDI framework offers a compelling new methodology for leveraging the full spectrum of domain features, paving the way for potentially transformative applications in DG and other related fields. Future work is set to explore the theoretical and practical challenges involved in further disentangling and leveraging these features.



