- The paper presents a novel direct S2ST method integrating a speech encoder, LSTM-based linguistic decoder, and duration-based acoustic synthesizer to improve translation quality.
- It employs an innovative voice preservation technique by using augmented training data and cross-lingual TTS models to maintain speaker characteristics.
- Experimental evaluations show enhanced BLEU scores and natural speech generation across multiple languages, outperforming cascade systems.
Translatotron 2: Direct Speech-to-Speech Translation with Voice Preservation
Introduction
Translatotron 2 represents a significant advancement in the domain of direct speech-to-speech translation (S2ST), a technology designed to overcome linguistic barriers by converting spoken words from one language to another without intermediate text representation. Historically, S2ST systems have relied on a cascade architecture comprising automatic speech recognition (ASR), machine translation (MT), and text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis. Translatotron 2 challenges this paradigm by offering a direct S2ST approach, improving upon its predecessor in both translation accuracy and speech quality. The model integrates a speech encoder, linguistic decoder, and acoustic synthesizer connected by a single attention module.
Methodology
Model Architecture
Translatotron 2 was meticulously designed to address inherent limitations of the original Translatotron. The model architecture consists of a speech encoder utilizing Conformer blocks, a linguistic decoder powered by LSTM layers, and an acoustic synthesizer that refines signal generation with a duration-based methodology. The single attention module harmonizes linguistic decoding and acoustic synthesis, simplifying the alignment between source and target speech.
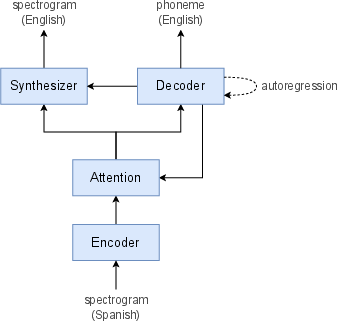
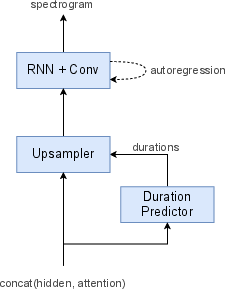
Figure 1: Overview of Translatotron 2.
Voice Preservation
A novel voice preservation technique enables Translatotron 2 to maintain the integrity of speaker characteristics seamlessly during translations, addressing privacy concerns and misuse potential associated with voice cloning technologies. The implementation utilizes augmented training data synthesized with consistent voice properties across languages, leveraging sophisticated TTS models capable of cross-lingual voice transfer.
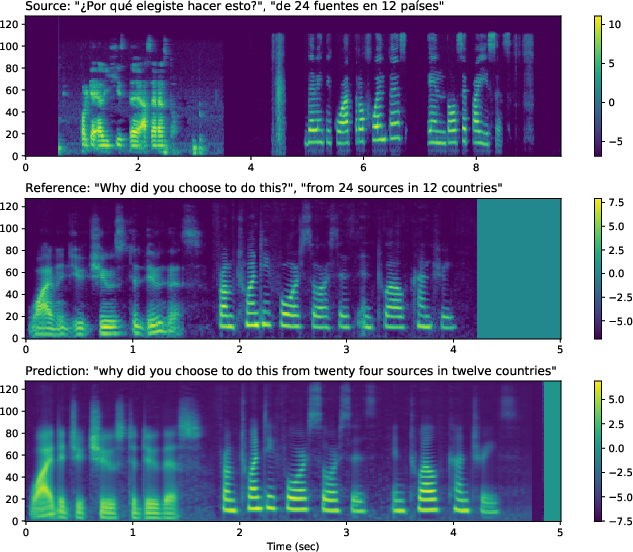
Figure 2: Sample mel-spectrograms on input with speaker turns. Translatotron~2 preserves the voices of each speaker in the translation speech.
Experimental Evaluation
Translation Quality and Speech Robustness
The experimental outcomes on datasets such as Fisher Spanish-English and CoVoST 2 demonstrate Translatotron 2’s performance superiority over its predecessor and potential competition with cascade S2ST systems. It achieves remarkable BLEU score improvements, showcasing enhanced translation precision. Moreover, the model mitigates over-generation errors such as babbling, presenting robustness comparable to well-established cascade models.
Natural Speech Generation
Subjective listening tests affirm the high naturalness of generated speech, substantiating Translatotron 2’s capability to synthesize audio that aligns closely with human-like speech quality, an essential requirement for practical deployment.
Multilingual Application
The model’s adaptability across multiple languages further attests to its versatility. Multilingual S2ST tasks reveal consistent performance enhancements, bolstered by architectural robustness and strategic augmentation techniques like ConcatAug, facilitating effective handling of speaker transitions.
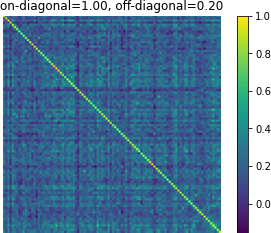
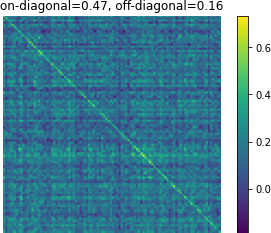
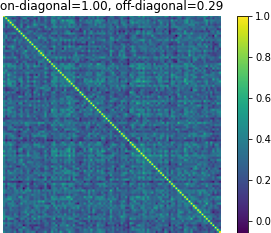
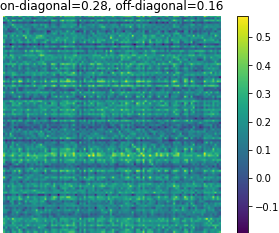
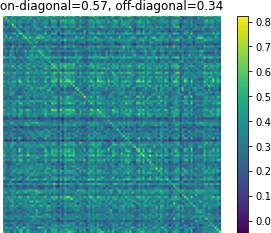
Figure 3: Affinity matrices of d-vector similarity among 100 random examples. Predictions from Translatotron 2 demonstrate clear preservation of speaker characteristics.
Conclusion
Translatotron 2 exemplifies significant advancements in direct S2ST, offering improved translation accuracy, naturalness, and voice preservation capabilities. Its innovative architecture addresses critical performance gaps and introduces robust solutions to privacy and misuse challenges. The versatility across languages supports a wide range of applications, paving the way for future developments in more inclusive and efficient language translation technologies.









