- The paper proposes a novel Courteous Virtual Traffic Signal Control framework that leverages deep reinforcement learning to manage unsignalized intersections.
- It models intersection management as a Markov Decision Process and employs proximal policy optimization with return scaling to stabilize learning.
- Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in throughput and reduced travel times in both simulated environments and real-world scenarios.
Courteous Behavior of Automated Vehicles at Unsignalized Intersections via Reinforcement Learning
Introduction
The gradual integration of Connected Autonomous Vehicles (CAVs) into road traffic presents a unique opportunity to enhance traffic management systems, particularly at unsignalized intersections. The research presented in "Courteous Behavior of Automated Vehicles at Unsignalized Intersections via Reinforcement Learning" (2106.06369) addresses the challenges associated with managing mixed traffic systems, where both human-driven vehicles (HVs) and CAVs coexist. The paper proposes a deep reinforcement learning approach to optimize traffic flow at unsignalized intersections by allowing CAVs to yield their right of way, thereby improving overall traffic efficiency and safety.
Methodology
The authors introduce a centralized intersection management method termed Courteous Virtual Traffic Signal Control (CVTSC), utilizing deep reinforcement learning to achieve cooperative behavior between CAVs and HVs. By modeling the intersection management task as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), the CVTSC learns policies to control CAVs, effectively acting as virtual traffic signals that prioritize yielding at intersections.
The solution involves defining a discrete action space for CAVs, specifying actions that allow or restrict passage on certain routes within the intersection (Figure 1). A critical aspect of the approach is return scaling, which addresses the imbalance of cumulative rewards at different states, ensuring stable learning dynamics across varying traffic demands. The paper also employs proximal policy optimization for learning the policy and value functions, benefiting from adaptive discounting to manage the variability in step lengths during training.
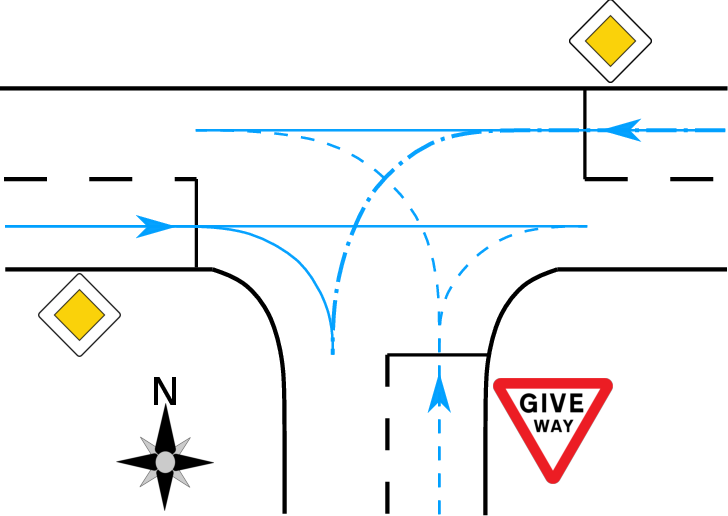
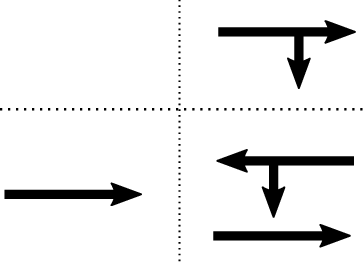
Figure 1: A typical three-way intersection illustrating priorities for lane management.
Results
Experimental evaluations conducted using the traffic simulator SUMO, both with simulated and real-world traffic data, exhibit significant improvements in traffic flow at unsignalized intersections managed by CVTSC. The approach demonstrates superiority over traditional road sign-based methods and adaptive traffic signal controllers across various CAV penetration rates.
The experiments reveal that CVTSC markedly improves both the efficiency and equity of the intersection management. At simulated traffic densities ranging from 500 to 3000 vehicles per hour, CVTSC consistently achieved higher throughput and reduced travel times compared to baseline methods (Figure 2).
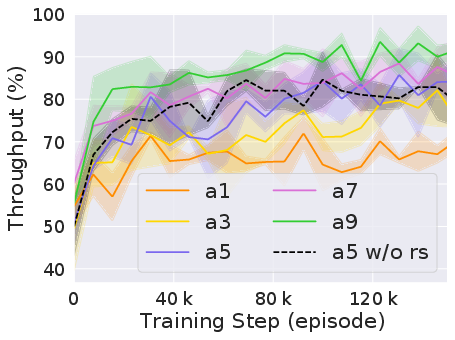
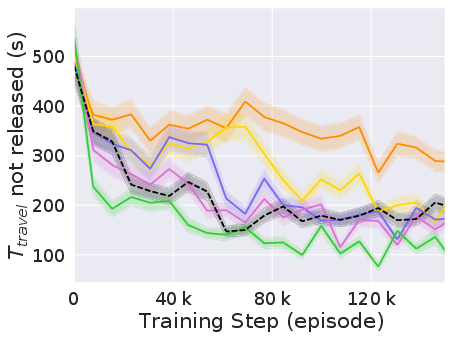
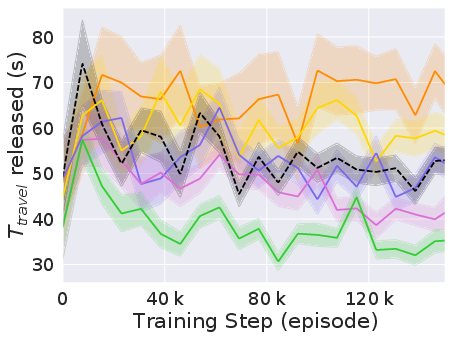
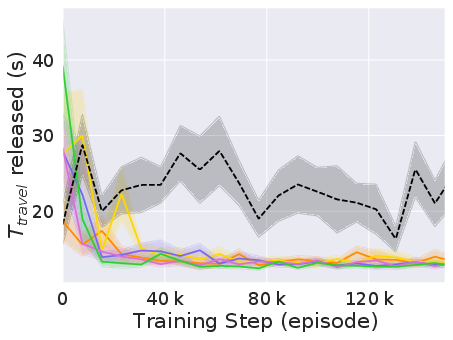
Figure 2: Performance of CVTSC compared to baselines in terms of vehicle throughput and travel time under varying traffic densities.
Real-world Application and Implications
The paper further evaluates CVTSC on real-world traffic data, specifically targeting an intersection in Freiburg, Germany (Figure 3). The results corroborate the simulation findings, with CVTSC effecting reduced travel times and increased throughput across different CAV penetration rates.
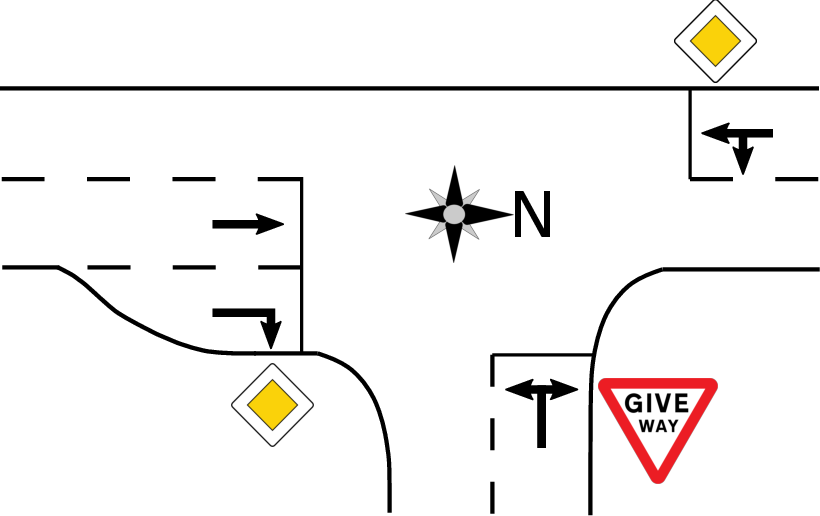

Figure 3: Real-world intersection layout used in the paper.
These findings illustrate the potential of reinforcement learning methods to effectively manage mixed traffic scenarios, highlighting practical applications of AI in traffic systems. The implications for urban planning include reduced environmental impact, enhanced safety, and improved public acceptance for CAVs.
Conclusion
The research outlines a robust framework for the management of unsignalized intersections in mixed traffic settings, providing a roadmap for future developments in AI-driven traffic systems. The integration of return scaling and deep reinforcement learning presents tangible benefits in optimizing traffic flow, paving the way for wider applications as the proportion of CAVs on roads increases. Future work could explore adaptation to more complex intersection layouts and integration with higher levels of vehicular automation. Additionally, ongoing research could focus on resolving communication challenges and increasing public trust in automated traffic systems.
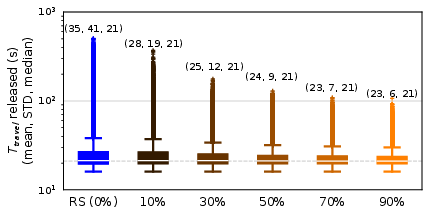
Figure 4: Box plot illustrating travel times in simulations using the real-world intersection.
In summary, the paper underscores the potential of reinforcement learning in facilitating courteous traffic management, aligning the multifaceted goals of efficiency, safety, and equity in modern vehicular networks.









