- The paper presents LemgoRL, a novel benchmark tool that integrates real-world traffic data into RL evaluation for traffic signal control.
- It employs PPO to achieve a 39.9% reduction in vehicle waiting time and an 87.7% drop in pedestrian waiting time compared to traditional methods.
- The study emphasizes safe phase transitions and regulatory compliance, laying the groundwork for real-world deployment of RL in urban traffic management.
Overview of Reinforcement Learning in Traffic Signal Control
The deployment of RL for traffic signal control (TSC) presents a novel approach to mitigating urban congestion while optimizing traffic flow at intersections. The paper "Towards Real-World Deployment of Reinforcement Learning for Traffic Signal Control" (2103.16223) introduces LemgoRL, a sophisticated benchmark tool designed to facilitate the transition of RL algorithms from theoretical simulation to practical, real-world usage. The town of Lemgo serves as the test case with a realistic model that captures the town's traffic dynamics.
Problem Statement and Background
Sub-optimal traffic signal controllers contribute significantly to urban congestion, hindering both environmental and public health. Traditional TSC policies typically hinge on pre-defined rules, struggling to adapt to dynamic traffic conditions. Traffic congestion alone can bear a hefty economic cost, such as the \$179 billion it imposed on urban areas in the United States in 2017. The deployment of RL in TSC has surfaced as a compelling method to generate adaptive and efficient control policies. However, existing RL applications frequently rest upon simplified traffic simulations, lacking the intricacies of real-world conditions.
LemgoRL: Bridging Simulation and Real-World Application
Design and Architecture
LemgoRL is meticulously crafted to emulate realistic traffic conditions in Lemgo, a medium-sized town in Germany. The essence of LemgoRL lies in its simulation model, created using SUMO, and its traffic signal logic unit (TSLU) programmed through LISA. This combination ensures that RL's application is both feasible and compliant with all safety and regulatory mandates.
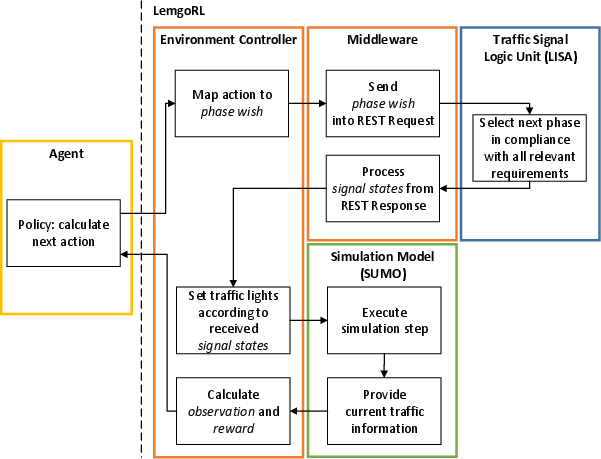
Figure 1: Process Diagram of LemgoRL highlights the interaction between its components.
LemgoRL uses state signals derived from real data during the afternoon rush hour, simulating a diverse suite of vehicle types and pedestrian movements. The subsequent realism furnishes RL agents a robust foundation for training and the expectation of better real-world adaptability.
Reinforcement Learning Framework
The fundamental premise of RL involves an agent that interacts iteratively with the environment, aiming to maximize cumulative rewards via policy optimization. An MDP encapsulates the traffic control problem, where decisions rely on state definitions composed of queue lengths, vehicular speeds, phases, etc., integrated within LemgoRL’s detailed simulation framework.
The RL agent benefits from a concrete reward function incorporating pedestrian waiting times, fostering more pedestrian-friendly outcomes, particularly significant in congested urban scenarios.
Transition Protocols and Real-World Deployment
Strategically designed phase transitions ensure LemgoRL adheres to safety requirements, even in the agent's absence. This capability underscores LemgoRL's intent for eventual real-world implementation, where field controllers and additional sensors will streamline RL policy applicability.
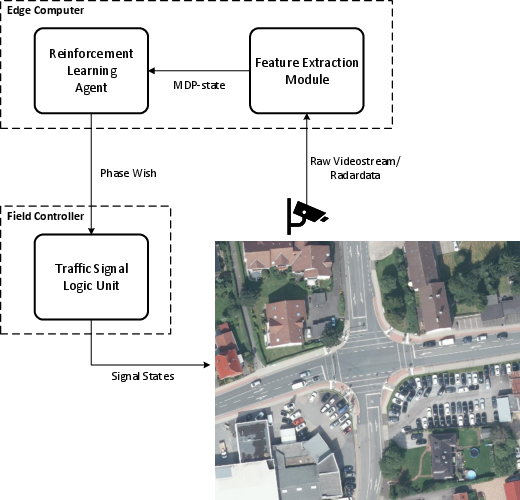

Figure 2: Schema for Real-World Deployment of LemgoRL provides a blueprint for integrating RL agents into existing infrastructure.
Evaluation and Results
A series of experiments bench-marking Deep RL algorithms such as PPO against conventional methods demonstrated RL's superior optimization capacity. Specifically, PPO achieved a 39.9% reduction in vehicle waiting time versus the second-best performing method and an astonishing 87.7% reduction for pedestrian waiting times when compared to fixed timings.
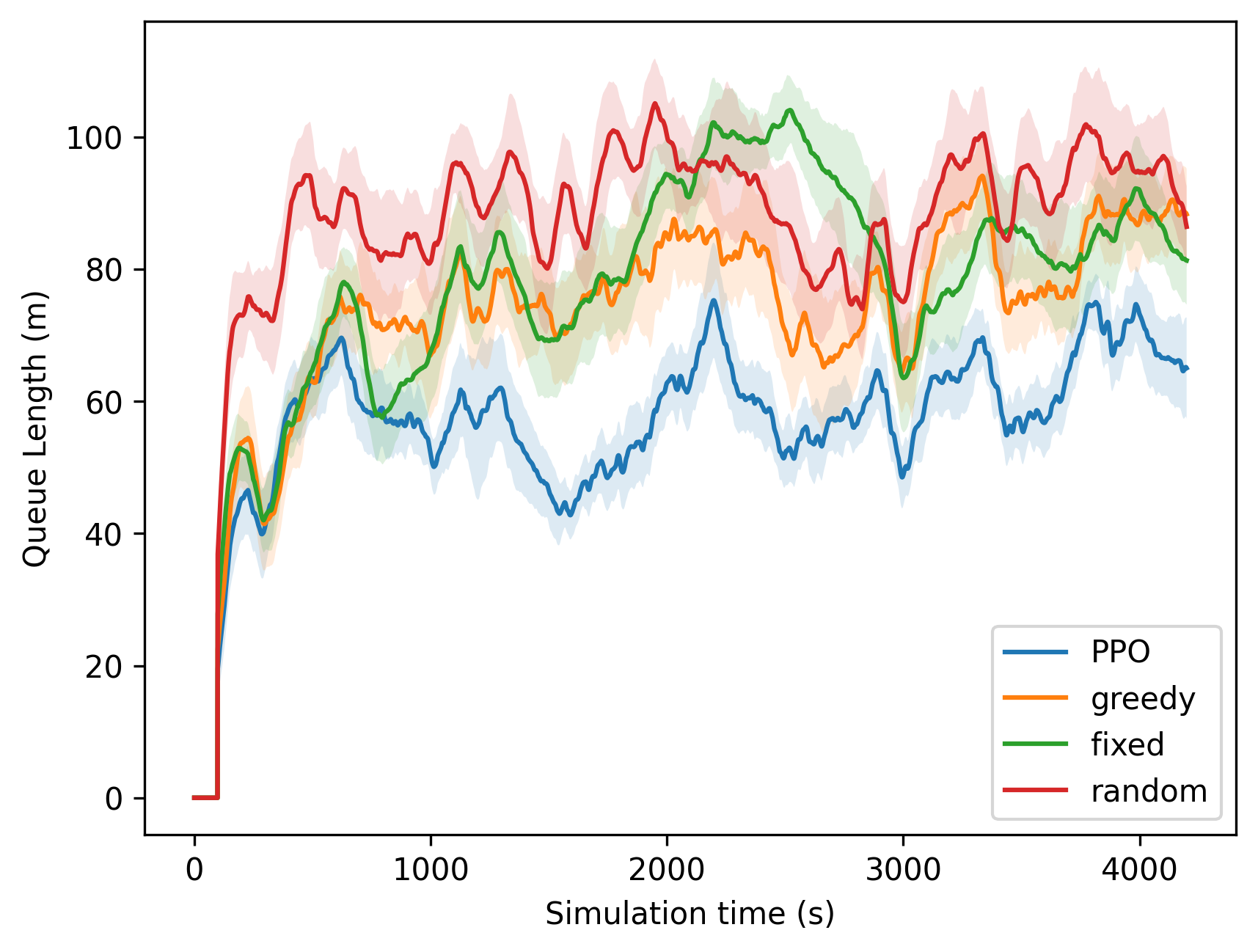
Figure 3: Queue Length\textsuperscript{5 shows PPO's superior performance over traditional methods.
Implications and Future Directions
The outcome from this study underscores the potential for RL to revolutionize TSC, offering insights into both technical advancement and the feasible transition to real-world deployment. LemgoRL is a pioneering development that positions RL as a formidable contender in real-time traffic signal management. Future strides will pivot towards deploying these research-based policies into urban settings, validating their practicality and efficacy over current systems.
Conclusion
The thrust towards bridging simulation-based RL with real-world TSC implementation has been effectively addressed through LemgoRL. This tool not only enhances our theoretical understanding but also paves the way for substantial practical advancements in intelligent transportation systems. As urban landscapes evolve, so too must the mechanisms that govern them, and reinforcement learning stands at the forefront of this evolution, poised to deliver real-time responsive traffic management solutions.




