- The paper introduces an integrated end-to-end framework that unifies license plate detection and recognition, improving efficiency in real-world applications.
- It employs a lightweight backbone and anchor-free detection with feature pyramid networks, achieving 97.5% detection accuracy and robust performance.
- Experimental results show real-time processing at 36 fps and high reliability under varied conditions, paving the way for practical ALPR deployments.
End-to-end Car License Plate Location and Recognition
Introduction
The paper "Towards End-to-end Car License Plate Location and Recognition in Unconstrained Scenarios" (2008.10916) presents a novel framework for simultaneous and real-time car license plate detection and recognition using a unified deep neural network. Auto License Plate Recognition (ALPR) systems are integral to Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) with applications in parking management, surveillance, and traffic control.
Conventional ALPR methods separate detection and recognition tasks and focus on specific scenarios, presenting challenges in real-world applications. These existing methods typically involve separate steps for license plate detection and character recognition, often relying on segmentation techniques, which can be sensitive to conditions like lighting and plate tilt.
The proposed framework is designed to efficiently handle these tasks concurrently, enhancing the adaptability of ALPR systems in unconstrained environments. The system utilizes an anchor-free method for plate detection, which mitigates sensitivity to adverse conditions, while a novel CNN branch performs character recognition. The recognition task is treated as a sequence labeling problem, employing Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) for character classification directly.
Methodology
Framework Overview
The proposed method integrates license plate location and recognition into a single end-to-end trainable network, which is both efficient and lightweight. This is achieved by using shared features and a multi-task learning strategy. It vastly simplifies pipeline architecture compared to traditional two-step solutions.
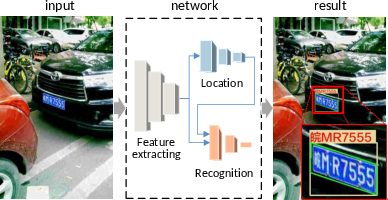
Figure 1: Schematic overview of our proposed framework. The input image is fed to a single neural network that consists of feature extracting, location, and recognition. The result includes a bounding box, corners, and characters.
Network Architecture
This integrated system employs a lightweight backbone network (ResNet-18) to efficiently extract shared features, using Feature Pyramid Networks (FPN) for fusion. The detection head predicts the bounding box and corners of the license plate using a center point and regression of relative position parameters, avoiding anchor boxes and IoU calculations.
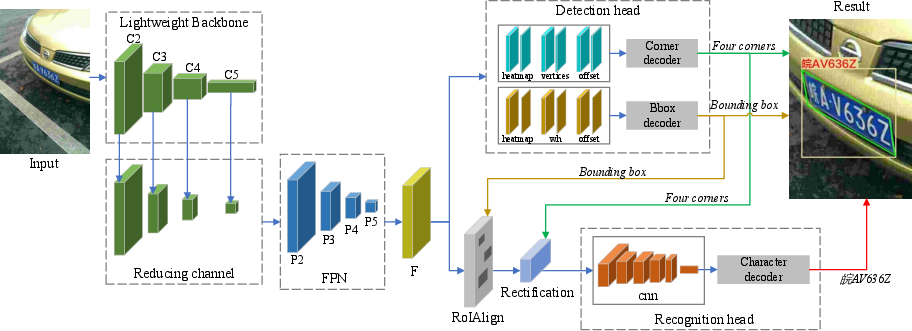
Figure 2: Proposed network for license plate location and recognition, employing FPN for feature extraction and sharing features for both tasks, enabling real-time operation.
A CNN-based recognition head decodes sequences using the CTC method, which facilitates direct sequence labeling and avoids character segmentation. This approach, combined with RoIAlign and rectification processes, ensures precision in recognition even under challenging conditions.
Loss Function and Optimization
Multi-task training optimizes location and recognition concurrently without NMS, using focal loss for detection and the standard CTC loss for recognition. The location task involves regressing bounding boxes and corner positions, while recognition uses sequence-level annotations with beam search for decoding.
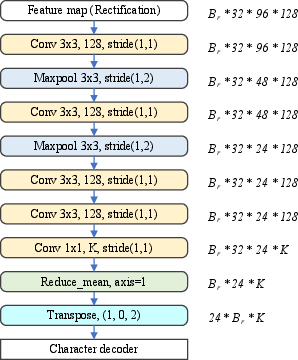
Figure 3: Proposed recognition head, detailing convolutional layers for further feature extraction and character decoding.
Experimental Results
The framework's efficacy was tested across multiple public datasets, such as CCPD, AOLP, and PKU vehicle datasets, demonstrating superior performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. On CCPD, significant improvements in detection (97.5%) and recognition (96.9%) accuracy were achieved with enhanced speed (36 fps on ResNet-18).
Table 1 and Table 2 illustrate the recognition and detection performance in challenging environments, validating robustness in varied conditions (e.g., weather, tilt, blur).
Implications and Future Work
The proposed approach advances ALPR systems by significantly improving the adaptability and efficiency of license plate recognition in uncontrolled scenarios. Its real-time processing capability makes it suitable for deployment in smart cameras and edge devices, highlighting its practical implications.
Future developments could explore multi-line plate recognition and application of similar methodologies in broader text spotting contexts. The requirement for large annotated datasets poses a potential research avenue for synthetic data usage or improved semi-supervised annotation techniques.
Conclusion
This end-to-end framework represents a significant step towards efficient, accurate, and real-time ALPR systems, overcoming limitations inherent in traditional separation of detection and recognition tasks. It offers superior accuracy in unconstrained scenarios, thus paving the way for practical deployment across various transportation and security applications.




