Transforming task representations to perform novel tasks
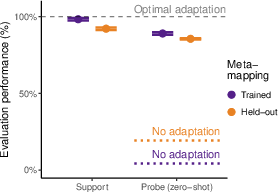
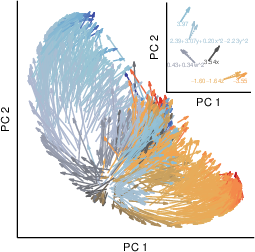
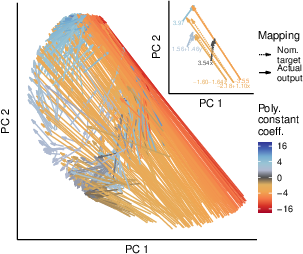
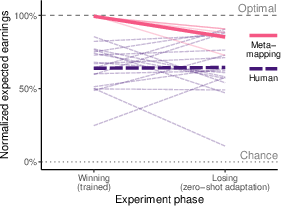
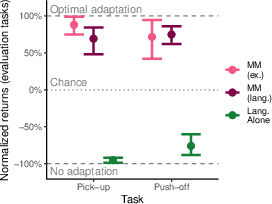
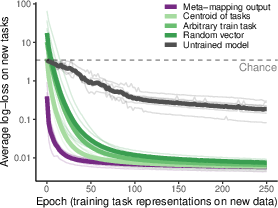
Abstract: An important aspect of intelligence is the ability to adapt to a novel task without any direct experience (zero-shot), based on its relationship to previous tasks. Humans can exhibit this cognitive flexibility. By contrast, models that achieve superhuman performance in specific tasks often fail to adapt to even slight task alterations. To address this, we propose a general computational framework for adapting to novel tasks based on their relationship to prior tasks. We begin by learning vector representations of tasks. To adapt to new tasks, we propose meta-mappings, higher-order tasks that transform basic task representations. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this framework across a wide variety of tasks and computational paradigms, ranging from regression to image classification and reinforcement learning. We compare to both human adaptability and language-based approaches to zero-shot learning. Across these domains, meta-mapping is successful, often achieving 80-90% performance, without any data, on a novel task, even when the new task directly contradicts prior experience. We further show that meta-mapping can not only generalize to new tasks via learned relationships, but can also generalize using novel relationships unseen during training. Finally, using meta-mapping as a starting point can dramatically accelerate later learning on a new task, and reduce learning time and cumulative error substantially. Our results provide insight into a possible computational basis of intelligent adaptability and offer a possible framework for modeling cognitive flexibility and building more flexible artificial intelligence systems.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.