- The paper introduces a gated mechanism within an attention-based framework to improve the fusion of textual, acoustic, and visual data.
- It employs separate Bi-GRUs and integrates self and cross attention to capture contextual features and enhance cross-modal interactions.
- Experiments show accuracy improvements of 1.6% on CMU-MOSI and 1.34% on CMU-MOSEI, validating the approach against established baselines.
Gated Mechanism for Attention Based Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
The paper presents an approach to enhance multimodal sentiment analysis by introducing a gated mechanism within an attention-based framework. This approach is applied to evaluate benchmark datasets CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI, achieving notable performance improvements over existing methods.
Introduction
The integration of textual, acoustic, and visual data for sentiment analysis has garnered significant attention due to the proliferation of multimodal data sources such as social media. Traditional approaches often fall short in capturing the complex interactions between these modalities, necessitating novel methods that can effectively learn cross-modal dependencies and manage the imperfections present in each modality.
Proposed Approach
The authors propose a comprehensive model for multimodal sentiment analysis that leverages a learnable gating mechanism to control information flow during cross-modal interactions. The primary components of the model include:
- Contextual Utterance Representation: Each modality is processed through separate Bi-GRUs to capture contextual features.
- Self Attention: This mechanism is employed to capture long-term dependencies across sequences of utterances, facilitating unrestricted information flow.
- Cross Attention: Explores interactions between different modalities, using co-attention matrices to generate cross-attentive representations.
- Gating Mechanism: A conditional gating mechanism modulates cross-modal interactions, thereby emphasizing useful information while mitigating noise.
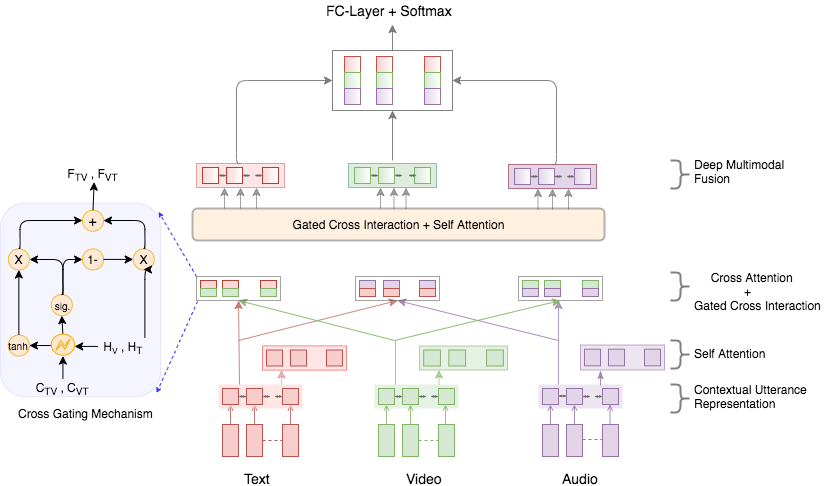
Figure 1: Architectural diagram of the proposed approach.
- Deep Multimodal Fusion: Combines self-attended and cross-attended features using a recurrent layer, resulting in deep multimodal contextual representations.
Experimental Evaluation
Experiments conducted on CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI datasets demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed approach.
- Performance Metrics: The model achieves 83.9% accuracy on CMU-MOSI and 81.1% accuracy on CMU-MOSEI, representing improvements of 1.6% and 1.34% over state-of-the-art methods, respectively.
- Baseline Comparisons: The paper includes ablation experiments to validate the contributions of self-attention and gating mechanisms, confirming their roles in enhancing model performance.
Benchmarking
The paper offers a comparison of the proposed method with several established baselines, notably Tensor Fusion Networks and Memory Fusion Networks. The results underscore the superiority of the gated mechanism in handling noise and ensuring robust cross-modal interactions, leading to better sentiment predictions.
Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative evaluations illustrate the model's ability to selectively weight modalities based on their contribution to sentiment inference. Examples highlight cases where textual cues alone were insufficient without complementary visual or acoustic data, or where cross-modal enhancement was unnecessary due to strong unimodal features.
Conclusion
This work introduces a gated mechanism that advances multimodal sentiment analysis by effectively exploiting cross-modal interactions and selectively mitigating the noise inherent to individual modalities. Future research directions could extend these techniques to environments with significant noise interference, such as real-world customer service interactions. The reported performance gains highlight the potential applicability of this approach across diverse sentiment analysis tasks.


