- The paper establishes that even single-hidden-layer networks with ReLU retain the universal approximator property for functions in L1.
- It demonstrates that softmax layers can approximate indicator functions, ensuring effective multi-class classification performance.
- The findings underscore the robustness of modern network architectures and suggest potential extensions toward deeper, more complex models.
Universal Approximation and Neural Network Architectures
The study presented in the paper, "On Approximation Capabilities of ReLU Activation and Softmax Output Layer in Neural Networks" (2002.04060) extends the universal approximation theory, a fundamental aspect of neural network capabilities, to configurations utilizing the ReLU activation function and softmax output layers. This examination provides theoretical insights into the approximation potential of these widely adopted components in modern neural network architectures, notably addressing their use in complex multi-class classification tasks.
ReLU Activation Function and Approximation
The unbounded ReLU activation function has rapidly become the preferred activation function in deep learning due to its significant enhancement of training convergence in deep networks. The paper demonstrates that neural networks employing ReLU, even when limited to a single hidden layer, retain the universal approximator property to approximate any function in L1. This conclusion is backed by Theorem 1 and relies on constructing a special activation function σ1(t) that leverages the piecewise linear nature of ReLU.
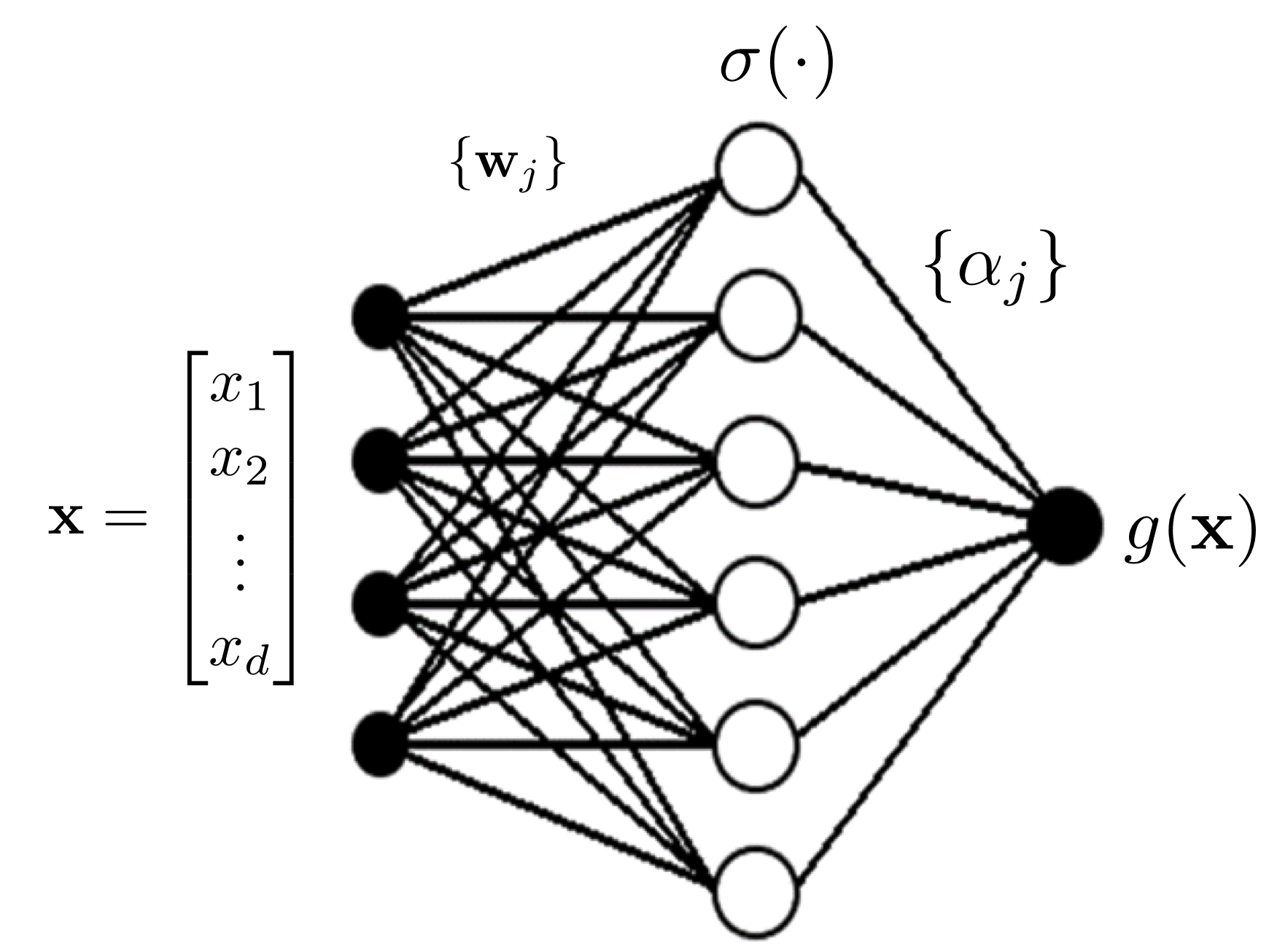
Figure 1: An illustration of a single-output feedforward neural network without any softmax layer.
The research extends the theoretical framework to multi-output networks, showing that any vector-valued function with components in L1(Id) can be effectively approximated. This aspect is crucial for the development of neural network models tasked with predicting multiple outputs concurrently.
Softmax Output Layer and Classification Tasks
The study explores the softmax output layer's theoretical justification, which is commonly used to interpret outputs in pattern classification scenarios where class probabilities are required. The softmax layer fundamentally transforms output ranges, thereby affecting the network's approximation capabilities.
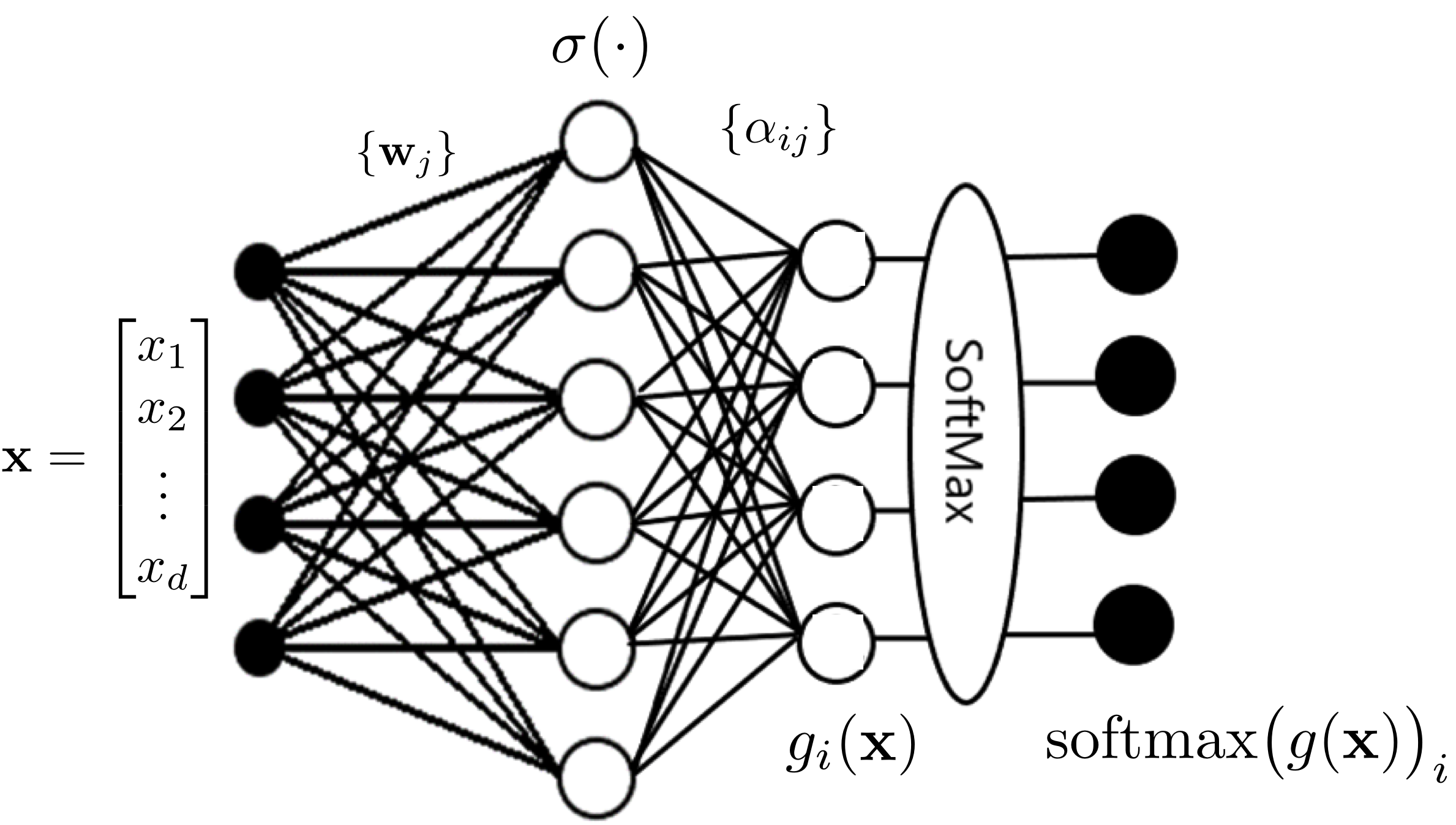
Figure 2: An illustration of a multi-output feedforward neural network with a softmax layer.
Utilizing the concept of indicator functions, which represent class labels as stark binary vectors, the analysis establishes that neural networks equipped with softmax can approximate these indicators in an L1 sense. The work leverages Lemma \ref{lemma-softmax}, ensuring that the network's softmax outputs approach the functional behavior of indicator vectors, reinforcing the efficacy of neural architectures in handling discrete multi-class outputs.
Implications and Future Direction
The findings of this paper have several implications for the design and application of neural networks:
- Theoretical Justification for Networks: The universal approximator property is secured even with ReLU and softmax, underpinning the robustness of modern network designs.
- Multi-Class Classification: The ability to approximate indicator functions validates the use of softmax layers in classification tasks involving exclusive class labels, a cornerstone of practical applications in computer vision and text processing.
- Expansion to Complex Architectures: While the results are shown for single-layer networks, the principles can extrapolate to deep networks, supporting the structural evolution of networks in research and commercial ventures.
Future investigations can explore extending these findings to further complex architectures and non-linear output configurations, probing potential in unsupervised representation learning and beyond.
Conclusion
The extension of universal approximation capabilities to ReLU activations and softmax output layers offers substantial theoretical validation for current neural network practices. These insights promote confidence in employing such configurations for multi-class classification, and lay a foundation for continued exploration of activation functions and output layers, shaping the future innovations in neural network architectures.



