- The paper presents an AI-driven health coach that adapts daily and weekly aerobic exercise goals based on personalized performance data.
- Key methodology includes a staircase model for aerobic capability and adaptive goal-setting validated by expert feedback and simulations.
- The 6-week evaluation demonstrates increased exercise engagement among sedentary participants with a mean usability score of 75/100.
Introduction
The paper investigates the development of an AI-based health coach, particularly targeting sedentary and overweight individuals to promote aerobic exercise as a healthy lifestyle. The intelligent agent is implemented through a mobile application, NutriWalking, which applies model-based adaptive goal setting. This agent tracks and revises personalized exercise goals for a trainee, with difficulty adjustments as trainees progress.
Methodology
Adaptive Goal Setting
The coach employs a structured computational approach to goal setting, which is divided into weekly and daily scheduling. It personalizes coaching by maintaining a parameterized model of a trainee's aerobic capability, adjusting goals based on observed performance.
The coaching strategy follows the principles of setting challenging yet attainable, specific, and proximal goals.
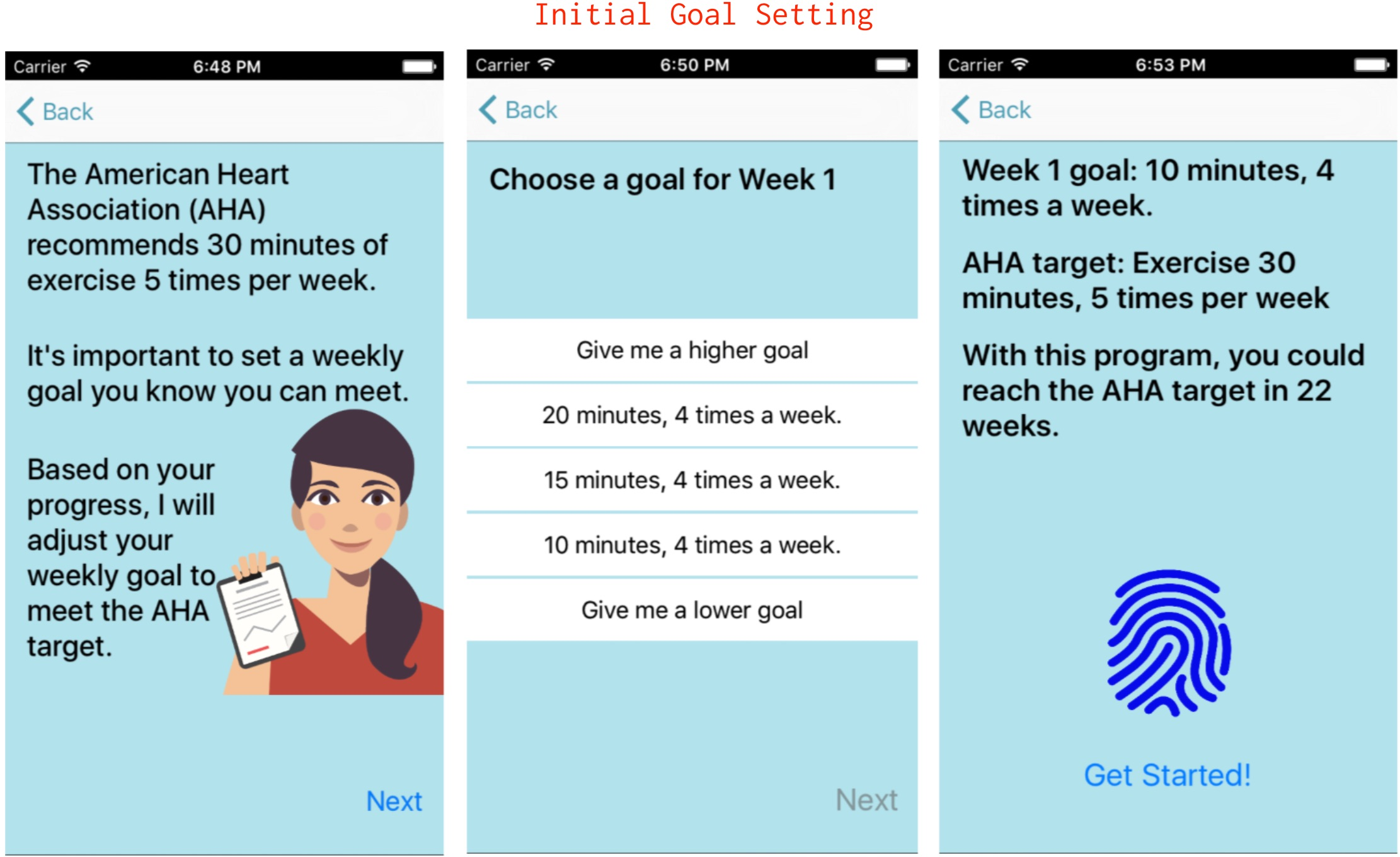
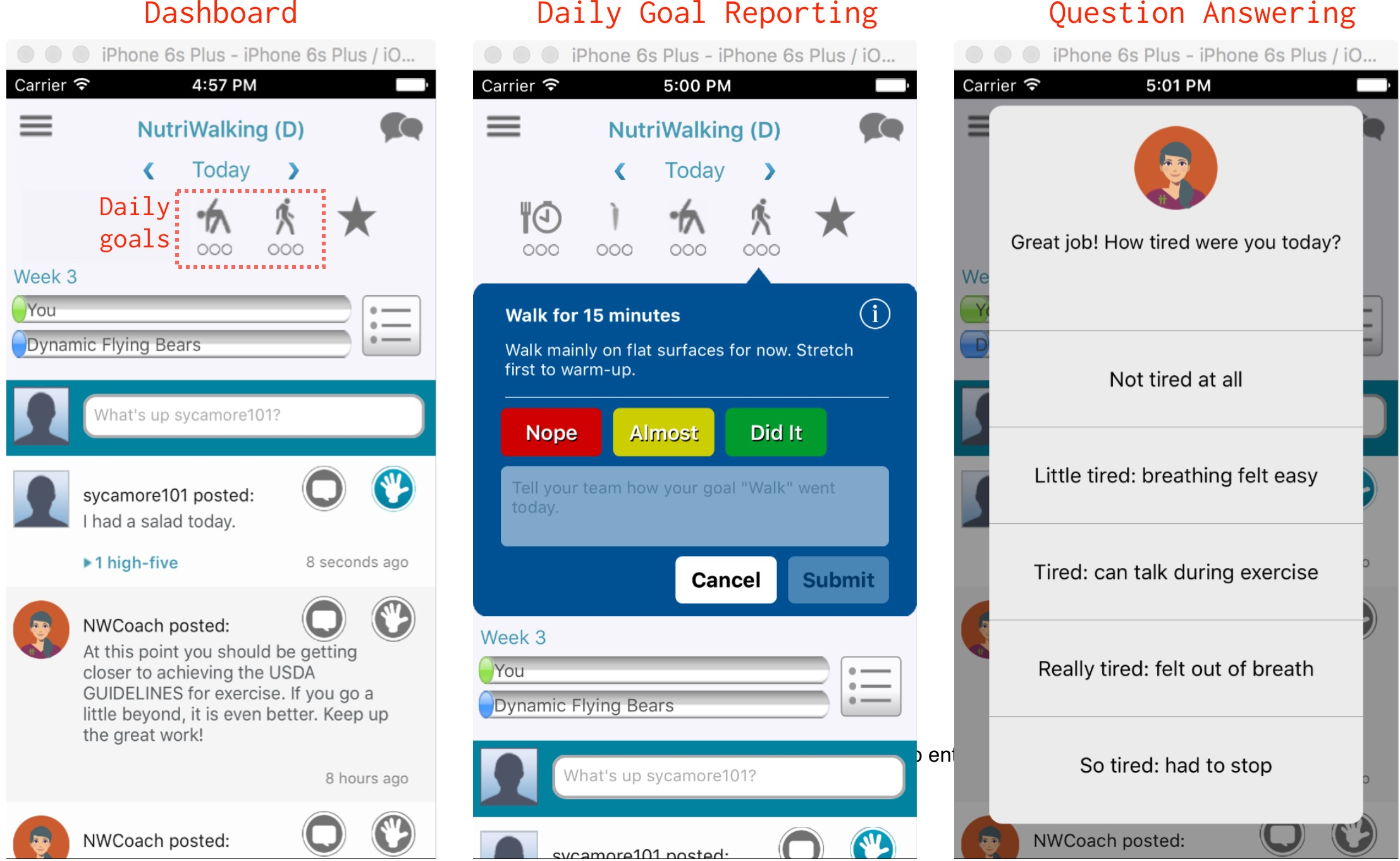
Figure 1: Various human-agent interactions NutriWalking - (top) initial goal setting, (bottom left) main dashboard, (bottom center) daily goal reporting, (bottom right) daily question answering.
Trainee Aerobic Capability Model
The paper presents a staircase model for aerobic capability growth, parameterized to represent variations in trainee profiles and capabilities. It uses model revisions to adapt the program as trainees progress or show variance in goal compliance.
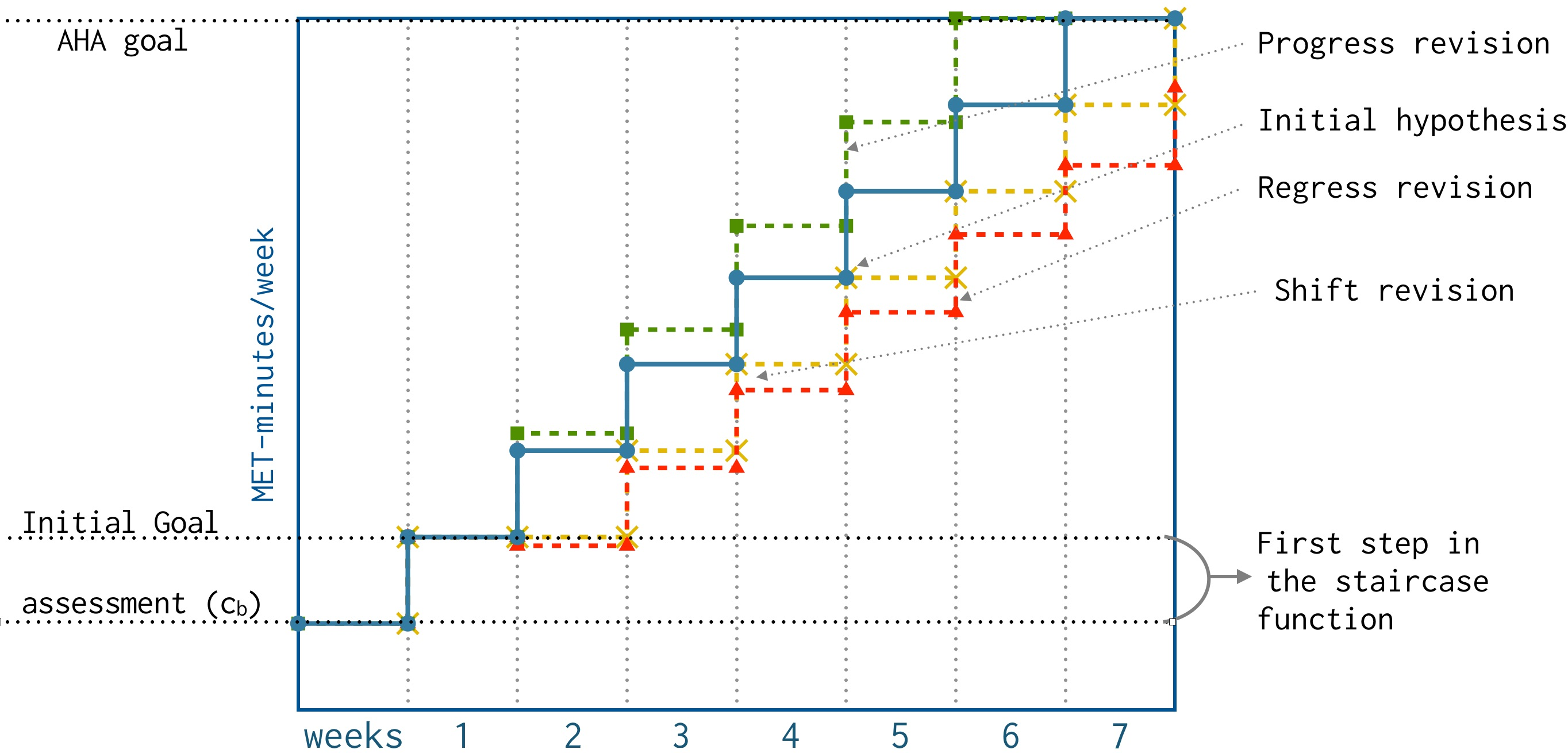
Figure 2: An adaptable model for aerobic capability. Blue line (CIRCLE) represents the staircase model for growth in capability and green (blacksquare), yellow (times), and red (blacktriangle) its revisions.
Evaluation
Adaptivity, Suitability, and Usability
The AI coach's adaptability was assessed through simulations of varying trainee profiles, capable of temporal and personal goal adaptations.
Empirical evaluations with expert physical therapists validated the suitability of the generated exercise goals, finding them to be safely attainable.
Usability studies exhibited positive feedback among individuals with type 2 diabetes or depression, who provided a mean System Usability Scale score of 75/100, indicating good acceptance.
Observed Impact Over 6 Weeks
Through a 6-week paper with sedentary participants, the adaptive coach demonstrated a positive effect on exercise volume. It suggested incremental goal adjustments and revealed participant engagement maintained throughout the program duration.
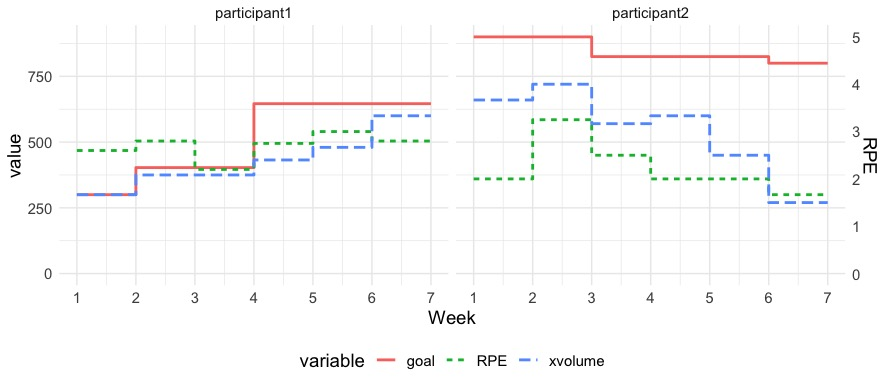
Figure 3: Weekly goals, exercise volume performed (xvolume), and rate of perceived exertion (RPE) of two participants for the length of the paper.
Limitations and Discussion
The research notes several limitations including reliance on self-assessment, the challenge of overly optimistic self-reporting skewing modeling accuracy, and platform constraints limited to iOS. Real-world applications presented some degree of trainee overestimation, necessitating a more accurate benchmarking process for initial aerobic capability.
The research advocates for broader inclusion of behavioral elements such as motivation levels and mood in future iterations, aiming to refine goal predictions and enhance program compliance and success.
Conclusion
The results of the paper underscore the potential for AI-driven solutions to support learning and adaptation in promoting healthier lifestyles via regular aerobic exercise. The NutriWalking intelligent coach proved to augment exercise through tailored goals for different individuals and contexts. Through continuous improvements and a comprehensive approach incorporating more interactive metrics, this AI methodology can foster significant societal health welfare advancements.





