- The paper introduces a regularization term that effectively mitigates mode collapse by promoting diverse outputs in conditional GANs.
- It achieves superior performance in image-to-image translation, inpainting, and future video prediction, as evidenced by improved LPIPS and FID scores.
- The method preserves the cGAN architecture without extra encoders, offering a practical and robust approach to enhance output diversity.
Diversity-Sensitive Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
Introduction
The research presents a method to address the mode collapse problem in Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (cGANs). Mode collapse, where the model fails to capture the diversity of the output distribution, is a significant limitation of existing cGANs that generate a single output per input, regardless of variations in the latent code. This paper introduces a simple regularization technique for the generator to induce diverse outputs based on latent codes, applicable to various cGAN architectures without architectural modifications.
Methodology
The proposed technique involves a regularization term added to the generator's objective, aiming to maximize the diversity of outputs by discouraging the generator from mapping latent codes to similar outputs. Mathematically, this is formulated as a maximization problem of sample output differences weighted by their latent code differences, controlled by a hyper-parameter λ. This approach directly addresses the inverse mapping issue without requiring an additional encoder network, hence maintaining simplicity and broad applicability.
Experimental Validation
The authors showcase the efficacy of their regularization technique across several conditional generation tasks: image-to-image translation, image inpainting, and future video prediction.
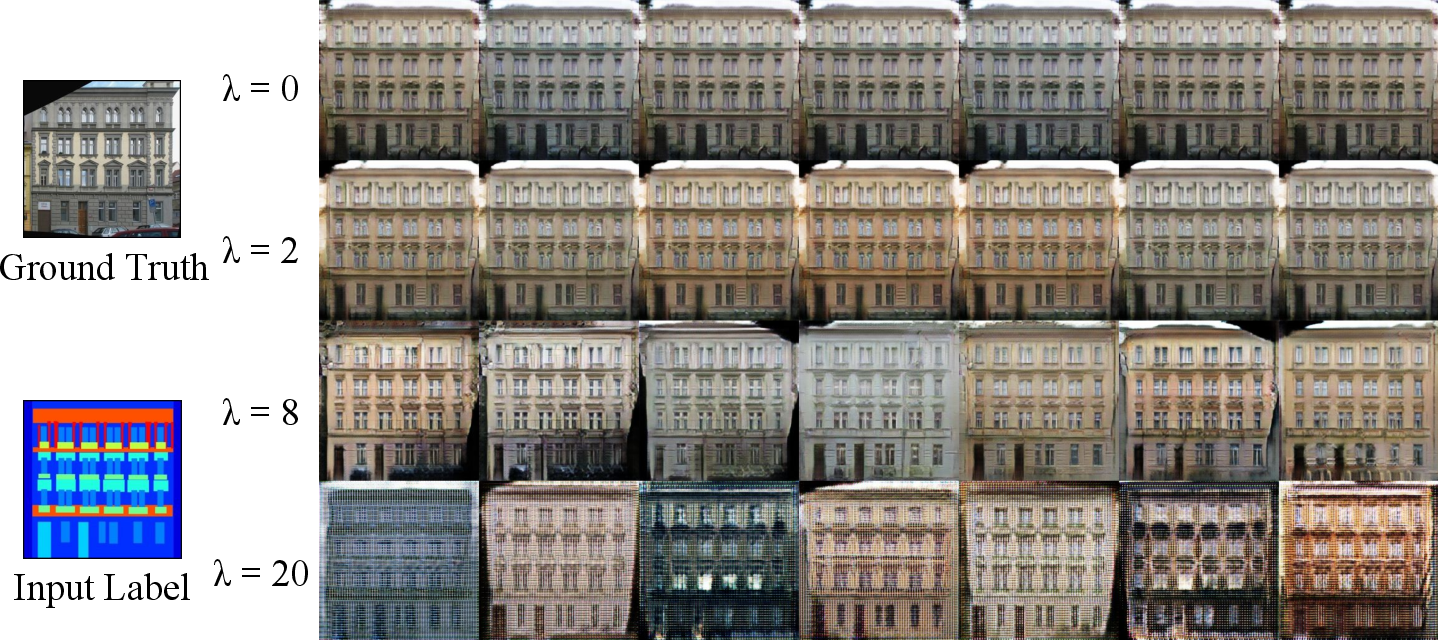
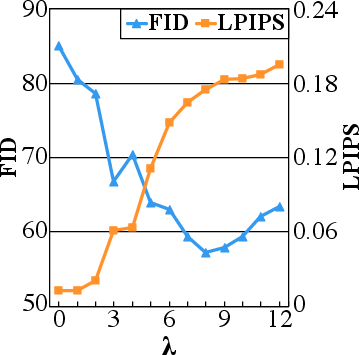

Figure 1: LPIPS and FID scores illustrate the diversity and quality of generated samples, respectively.
In image-to-image translation, the method significantly outperforms BicycleGAN and other existing approaches, both in quantitative metrics like LPIPS and FID and in qualitative human assessments. The latent space interpolation results show smooth transitions in generating diverse outputs, highlighting the generator's capacity for meaningful diversity extraction.
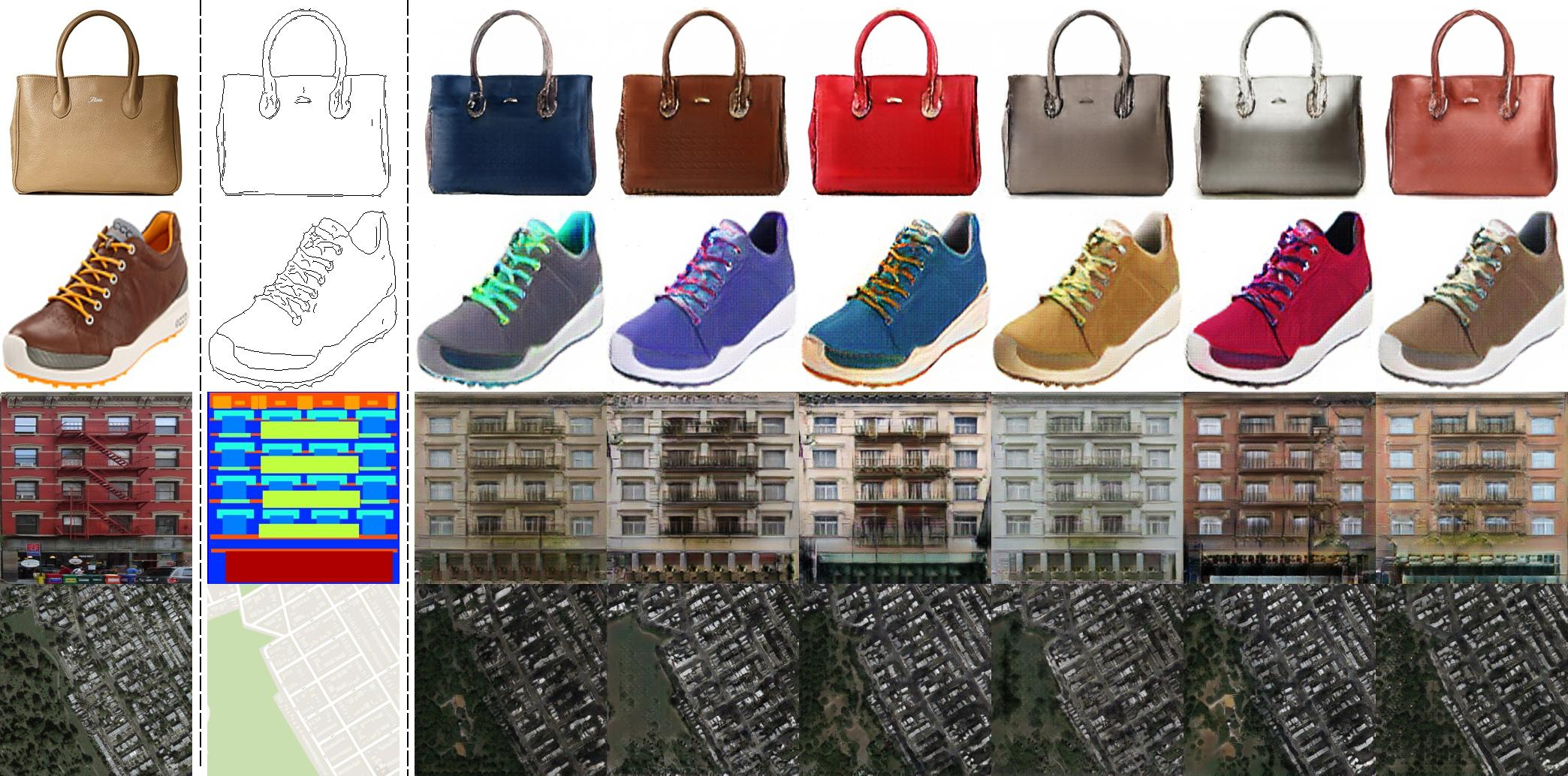

Figure 2: Diverse outputs generated by DSGAN. The first and second column shows ground-truth and input images, while the rest columns are generated images with different latent codes.
For image inpainting, where predictions of missing regions in images are required, the model achieves higher FID and LPIPS scores compared to the baseline, proving its superiority in generating diverse and semantically varied outputs.
In future video prediction, the model creates more realistic and diverse sequences than established techniques. The robustness of variance in predictions demonstrates potential improvements in capturing complex temporal dynamics in video data.

Figure 3: Stochastic video prediction results. Given two input frames, we present three random samples generated by each method. Compared to the baseline that produces deterministic outputs and SAVP that has limited diversity in KTH, our method generates diverse futures in both datasets.
Theoretical Insights
The paper provides a detailed analysis of the proposed regularization's impact on the generator's gradient and its effect on the mode collapse phenomenon. By ensuring a more substantial gradient norm for the generator, the approach addresses gradient vanishing issues prevalent in GAN training, fostering better exploration of the data manifold.
Implications and Future Research Directions
The extension of the proposed diversity-sensitive regularization method across varied objectives and network architectures is profound. It facilitates the balance between visual quality and diversity control and enhances the capacity of cGANs to model complex, multi-modal distributions. Future work could explore automated tuning of the key hyper-parameters λ and τ to dynamically align generated distributions more closely with actual data distributions, refining both realism and diversity in generative models further.
Conclusion
This paper successfully demonstrates a practical and effective method for mitigating the mode collapse in cGANs across multiple generative tasks. Through its intuitive yet potent regularization technique, it opens pathways for more reliable and versatile applications of GANs in diverse conditional generation domains.





