- The paper introduces a novel heuristic that uses cosine gradient similarity to adaptively weight auxiliary losses for better convergence.
- It provides theoretical justifications showing that positive gradient alignment reinforces main task performance while mitigating negative transfer.
- Experimental results in both supervised and reinforcement learning settings demonstrate enhanced learning speed and improved task performance.
Adapting Auxiliary Losses Using Gradient Similarity
Introduction
The paper proposes a method designed to enhance the data efficiency of neural networks by judiciously utilizing auxiliary losses that supplement the main task. An auxiliary loss can potentially hinder the main task; thus, identifying when and how an auxiliary task is beneficial is essential. The technique introduced leverages gradient similarity, specifically the cosine similarity between the gradients of the main and auxiliary tasks, as a measure to determine the effectiveness of the auxiliary loss throughout training.
Cosine Similarity Method
The core of the implementation involves computing the cosine similarity between the gradients of the main task and the auxiliary task. It acts as a heuristic to modulate the influence of the auxiliary loss based on its alignment with the main task gradients. If the cosine similarity is positive, implying beneficial alignment, the model incorporates the auxiliary gradient into the training process. Conversely, if negative, the auxiliary gradient is disregarded to prevent adverse effects. This approach guarantees convergence to critical points of the main task, effectively managing the auxiliary loss based on task alignment rather than constant hyperparameters.
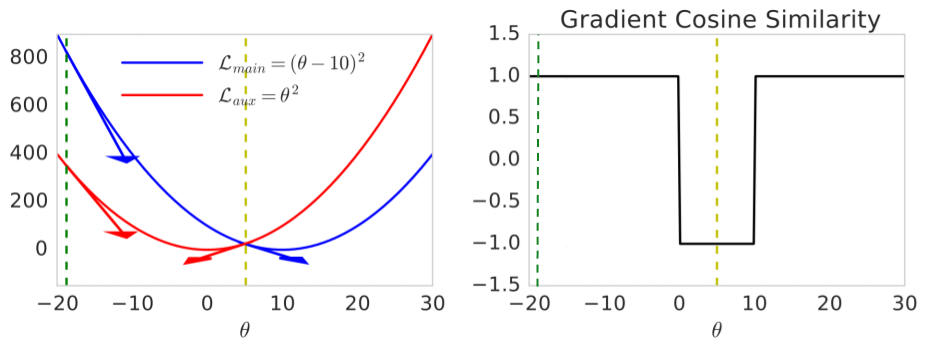
Figure 1: Illustration of cosine similarity between gradients on synthetic loss surfaces.
Theoretical Justifications
The method is supported by several propositions that demonstrate convergence under certain conditions. The formulation ensures that integrating auxiliary task gradients occurs in such a manner that it does not detract from the optimization of the main task. Notably, the method accounts for scenarios where gradient estimation may be noisy, adapting dynamically to ensure stability and convergence.
Practical Applications and Results
The technique was validated through experiments spanning supervised learning and reinforcement learning (RL). In RL, the method adeptly adjusted auxiliary losses from teacher policies, yielding improvements in learning speed and task performance without suffering from negative transfer. In supervised learning settings, it managed auxiliary losses to optimize the training process effectively.
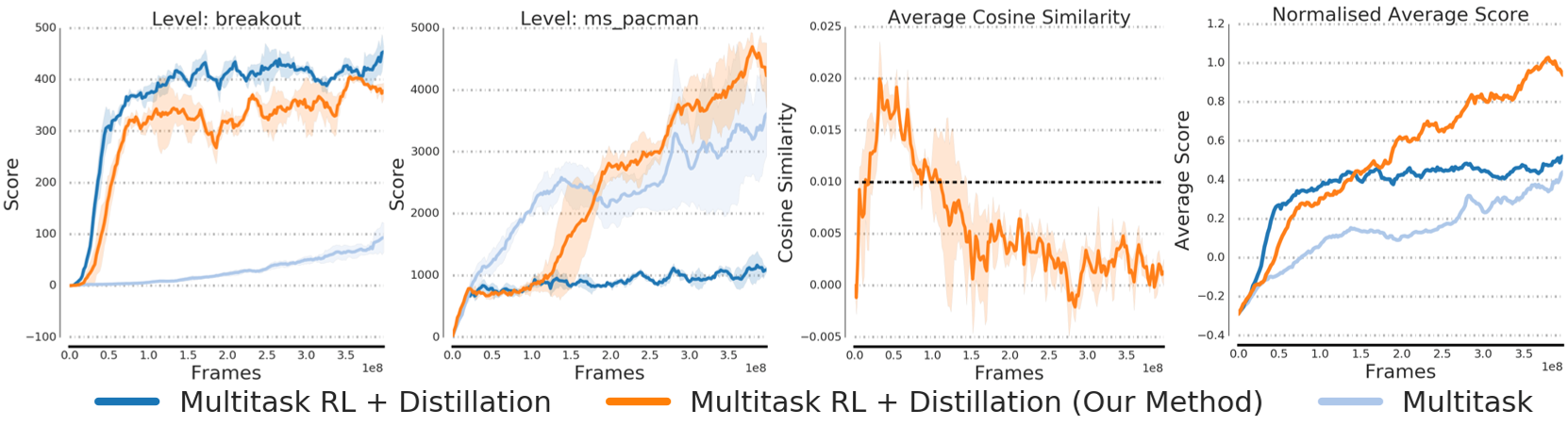
Figure 2: Results on Breakout and Ms. PacMan: Our method learns both games without forgetting and achieves the best average performance.
Discussion of Challenges
The deployment of gradient similarity in high-dimensional spaces was explored, showcasing its reliability even when gradients appear orthogonal due to dimensional complexity. Noise handling in estimation, potential impacts on optimizer statistics, and slow learning cases were discussed, alongside providing mitigation strategies. Despite the intricacies, empirical evidence suggests the heuristic to be robust across varied neural network configurations and training setups.
Conclusion
The paper presents a compelling strategy to align auxiliary losses dynamically based on gradient similarity, thus enhancing training efficiency and effectiveness. This modulation prevents negative transfer and fosters positive transfer, optimizing learning outcomes across domains. Future work could address scenarios with initial negative transfer but potential benefits later, expanding the heuristic's utility.
In closing, the cosine similarity method demonstrates substantial promise in adaptive loss management, warranting further exploration and refinement in real-world neural network applications.

