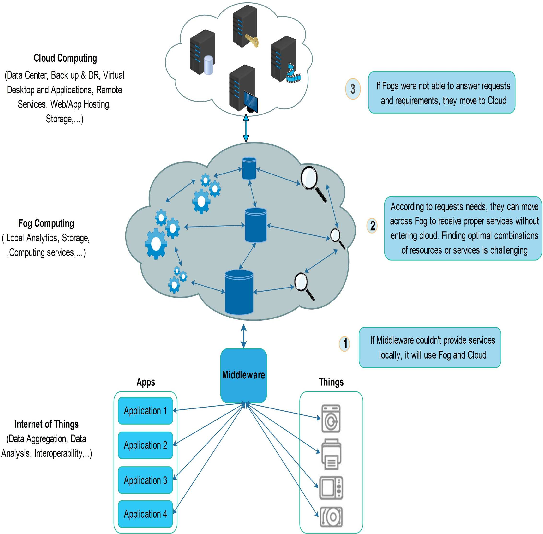
- The paper presents a comprehensive review on middleware technologies for Cloud of Things to overcome IoT heterogeneity and scalability challenges.
- It evaluates diverse architectural models—from component-based to centralized—to ensure modularity, real-time processing, and seamless integration.
- It highlights critical concerns in security, privacy, and resource management while outlining future directions for robust CoT deployments.
Middleware Technologies for Cloud of Things - A Survey
Introduction
The concept of the Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping the future of communication networks, allowing a multitude of interconnected 'smart' objects to seamlessly interact. This vast IoT network is anticipated to consist of over 50 billion devices by 2020. However, the scalability and resource limitations of IoT present significant challenges. With this complexity in mind, Cloud of Things (CoT) emerges as a promising solution by integrating cloud computing into IoT ecosystems to address challenges like heterogeneity, data storage, processing, and security. This survey provides a comprehensive analysis of middleware technologies vital for CoT systems.
The Role of Middleware in CoT
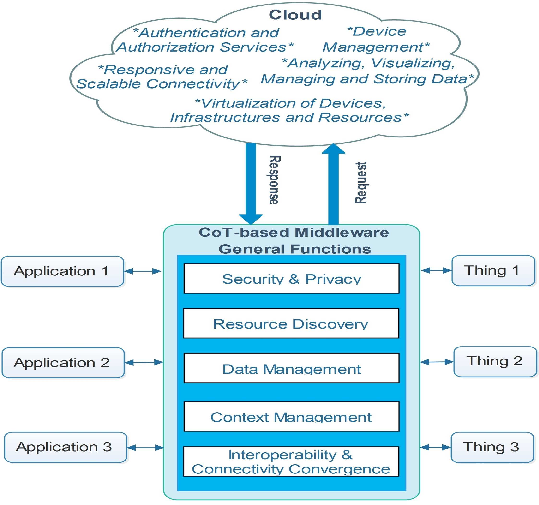
Middleware is a pivotal software layer positioned between IoT devices and cloud-based applications, aiming to solve interoperability issues and provide a stable communication platform. Middleware technologies in CoT environments must address key challenges such as heterogeneity of devices, interoperability among disparate systems, and secure, reliable data handling across diverse platforms.
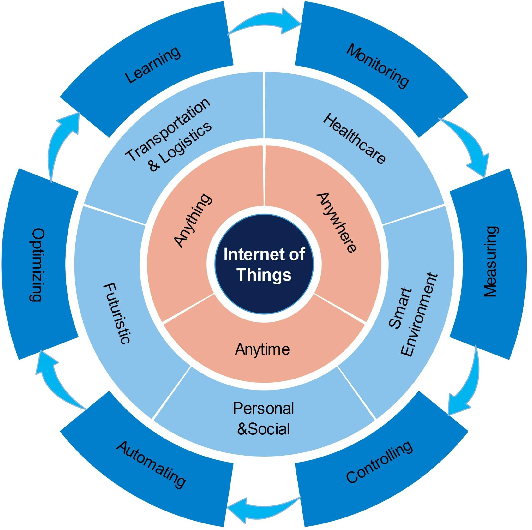
Figure 1: Internet of Things - main concept and functionalities.
One of the critical functions of middleware in CoT platforms is to offer abstraction, effectively hiding underlying technical complexities from application developers and end-users while facilitating seamless integration of new services. The survey identifies several essential features of CoT middleware including:
- Flexibility and Transparency: Enables system adaptation to dynamic networks and environments, masking the complexities of device heterogeneity.
- Context Management and Interoperability: Ensures coherent data integration and communication across different device platforms and systems.
- Adaptability and Resource Efficiency: Middleware must allow real-time adaptation and efficient resource utilization, essential for highly dynamic environments typical of IoT systems.
Architectural Styles in Middleware Design
The survey categorizes middleware architectures into various styles, each suited to different application demands and operational environments. Key architectural styles include component-based, distributed, service-based, node-based, centralized, and client-server models.
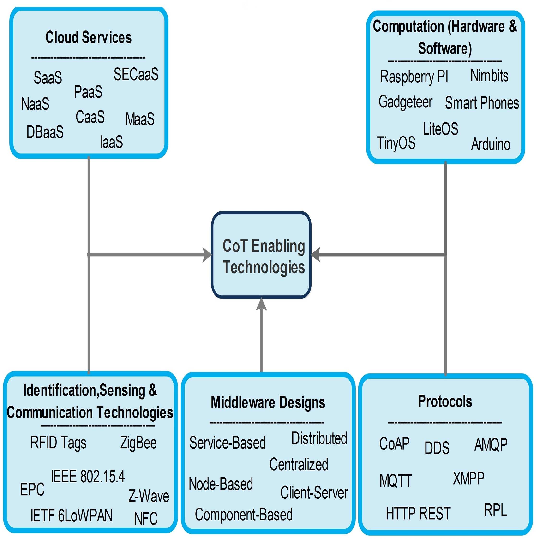
Figure 2: CoT enabling technologies.
Evaluation of Middleware Solutions
Several middleware solutions are evaluated, illustrating varied applications and capabilities:
- Carriots: Specializes in M2M communications and smart city applications through a cloud-based PaaS.
- ThingWorx and Xively: Provide extensive support for real-time data processing, big data analytics, and broad device compatibility.
- C-MOSDEN and OpenIoT: Focus on mobile sensing and cloud integration, enabling efficient data handling in smart environments.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite advancements, several challenges remain in middleware development for CoT:
Conclusion
Middleware technologies in Cloud of Things environments provide essential support for integrating vast networks of IoT devices with cloud computing infrastructure. While these technologies pave the way for advanced applications in smart cities, healthcare, and industrial IoT, the ongoing work addressing scalability, real-time constraints, and security will further enhance their effectiveness and adoption. Future research must continue to evolve these technologies to meet the growing demands of rapidly expanding IoT landscapes.